How to write an effective project report?

Often neglected because it is time-consuming and offers results that can only be observed in the long term, the project assessment remains essential. Essential to successful project management , it reviews everything that worked well and especially the points of optimization in order to propose concrete corrective actions for future projects. A reference for the preparation of similar projects, it helps to save time and performance.
So, how do you make a project assessment ? In this article, we offer you a guide to understand its objectives as well as the best practices for writing an effective project report .
What is a project review?
🔎 Synonyms: project report, project evaluation, project debrief, project closure
The project report, or end-of-project report, is the main document of the close-out phase. This summary analyzes the successes and challenges encountered throughout the project. Honest and transparent, the project report evokes the positive as well as the negative in order to establish a realistic and critical synthesis of the project.
In addition, the end-of-project report marks the official closing of the project, where the client acknowledges receipt and approves the deliverables. In addition, this phase also includes the archiving of documents as well as the closing of contracts.
What are the objectives of a project review?
What is the objective for the project team?
- Measuring performance
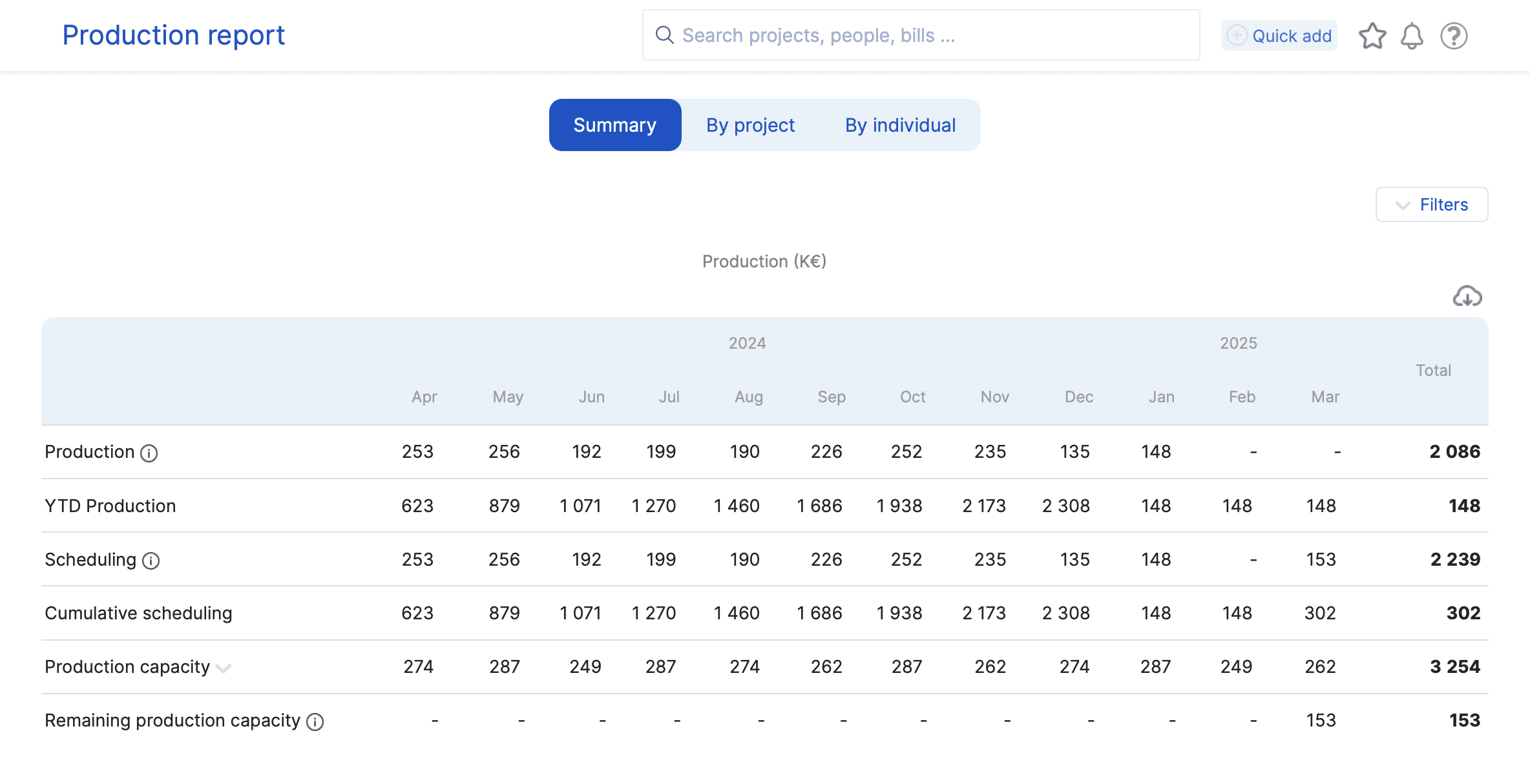
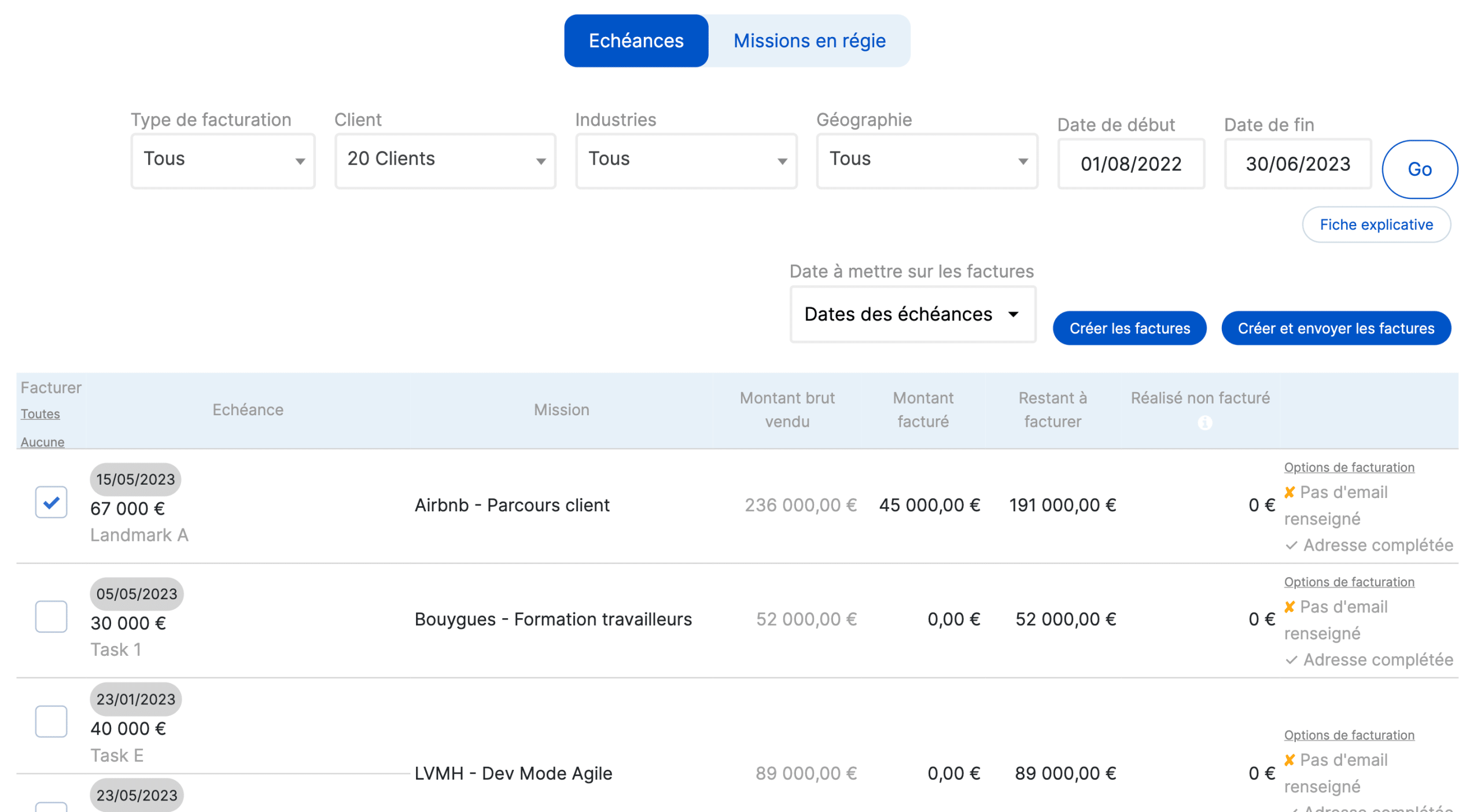
The project review reviews the creation of relevant production reports facilitates this evaluation.
Generated from a project management tool such as Stafiz, you can compare the production carried out with that initially planned. Stafiz offers granularity by assignment and by employee, thus offering maximum transparency.
Finally, the project review is an opportunity to check that everything is in order, including that all invoices have been paid. You can also save time on this step throughout the project by using an automated invoicing system, combined with rigorous budget monitoring.
How to make a project assessment?
When should you take stock of a project?
Carried out during the project closure phase, the project assessment must however be done "cold". Avoid planning it directly after the last tasks have been completed and wait for the pressure to subside to achieve maximum objectivity.
However, the project review sometimes requires hindsight when certain information can only be observed in the long term. In this case, inform the team, record the initial observations and plan the next steps.
Who should participate in the project review?
All stakeholders participate in the project review:
- the project manager,
- team members,
- external service providers,
- the experts,
- the sponsor,
- the customer,
- the Project Management Officer (PMO).
A specialized coach can sometimes be relevant to play the role of facilitator thanks to his neutrality, thus trying to bring frankness and honesty.
The project balance sheet must allow all points of view to be obtained in a transparent manner. One-on-one interviews will help you get candid feedback. You need to build trust where teams feel comfortable enough to open up.
What steps are essential to carry out the project assessment?
The project assessment requires certain steps to be carried out upstream.
- Planning in the agenda, right from the planning phase. This ensures that all stakeholders are available.
- Once the project is delivered: the approval of the stakeholders. They validate the achievement of objectives. Completed and signed minutes formalize this step, ensuring that the project has been delivered, that the deliverables are compliant and unreserved.
- Archiving documents, so that decisions are recorded.
- The release of resources, which can then be reallocated to other projects.
- Administrative and contractual closure : payment of invoices, end of contract with service providers and suppliers, revocation of access. This step is essential to limit the risk of litigation.
What to put in a project report?
The project report records the opinions of all stakeholders.
Frameworks exist to facilitate exchanges and obtain constructive opinions:
- the Mad, Sad, Glad method,
- the framework Liked, Learned, Lacked and Longed For,
- the Drop, Add, Keep, Improve technique.
Here are the different parts that the project report includes.
The context of the project
Recall all the contextual elements that will allow you to understand the challenges of the project, even in 6 months or 2 years. Mention this way:
- the main objective,
- the perimeter,
- the actors involved (sponsor, project manager, project team, etc.),
- duration and dates,
- the tools used.
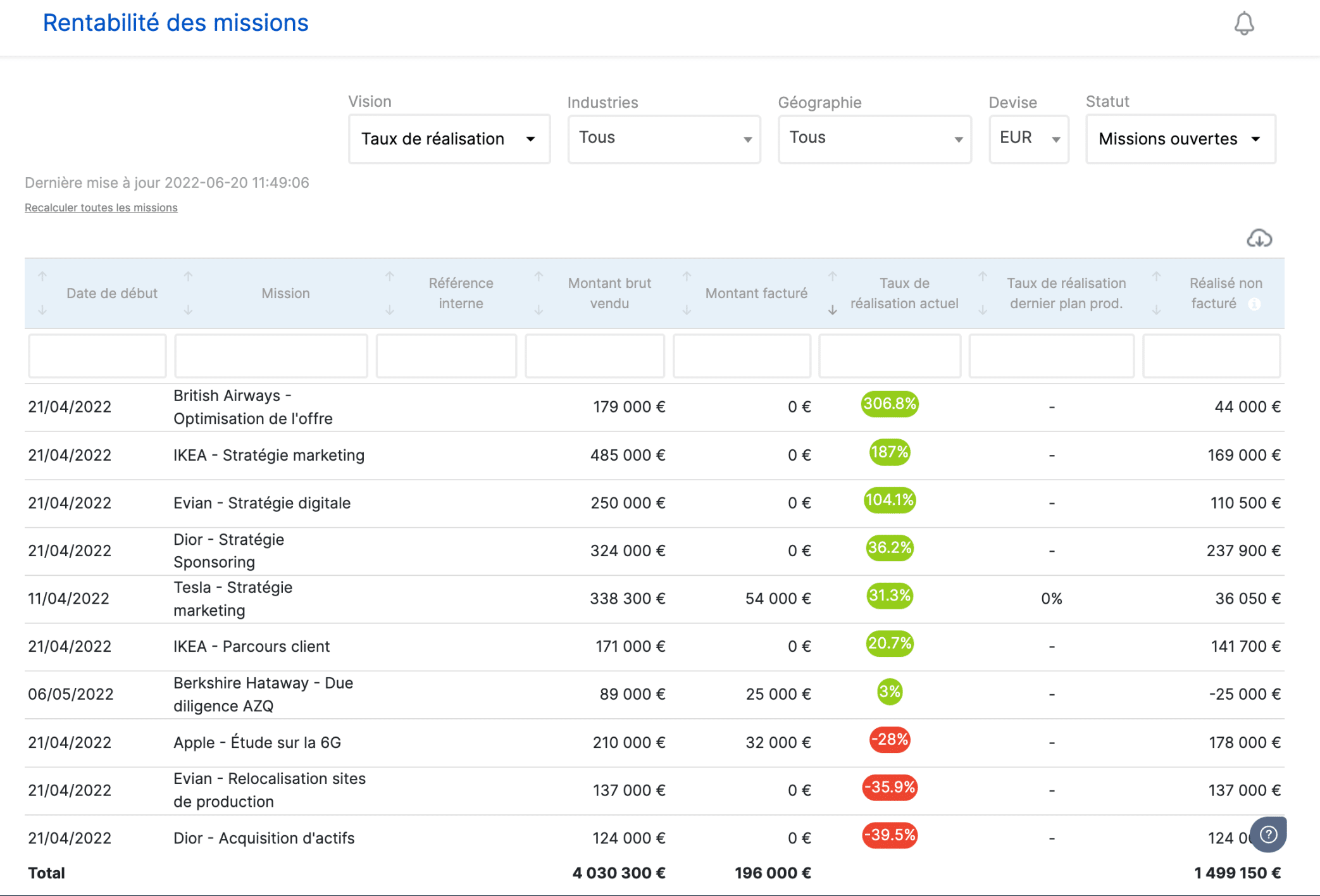
Gap analysis
This part allows you to quickly understand the discrepancies between:
- the forecast and the actual on budget,
- deadlines,
- quality.
This allows you to assess whether the objectives have been met, not achieved or exceeded.
Risk management analysis
Here, it is a question of reviewing the risks identified during the project scoping note.
- Did they finally take place?
- Have they been brought under control? If so, how?
- What was their impact on the project?
- Have other unanticipated risks emerged?
This analysis will allow you to take a step back and facilitate the risk management of subsequent projects.
Resource analysis
Resource analysis is the process of looking at the resources that are planned versus those actually used, for the project as a whole as well as for each task or milestone.
Also consider whether the workload consumed matches the workload billed.
Project planning software with time tracking features like Stafiz will help you get reliable and accurate data.
Analysis of deadlines
Does the expected end date match the actual delivery date?
If the answer is no, a thorough analysis of the causes of such a delay should be conducted.
The technical assessment
Have the technical choices made made it possible to meet the needs? Were these the most relevant solutions?
Take the time to analyze with the help of the experts involved in the project the other options that could have been considered.
The methodological assessment
In the same way, carry out the methodological assessment by taking into account the project management method used, the management and communication tools, and the processes.
The level of satisfaction of the sponsor
This part requires the involvement of the customer. We suggest offering them a satisfaction questionnaire with open-ended questions, allowing us to collect their remarks, suggestions, level of satisfaction and above all, the likelihood that they will recommend or use your services again.
Lessons learned
This decisive part consists of summarizing point by point all the lessons learned, whether they are failures or successes, and this on all aspects of the project:
- the organization,
- customer management,
- or team management.
The project manager's general summary
Written by the project manager, the summary concludes the project report by:
- confirming the acceptance of the project by the client,
- verifying that their expectations have been met and their level of satisfaction,
- Reviewing the quality of the deliverables,
- identifying areas for improvement,
- analysing the coordination of the teams.
Finally, the project manager shares his or her overall feedback, thanks the teams and proposes concrete actions in a continuous improvement approach.
What are the steps after writing the project report?
After writing the project report, it is essential to share it in order to maximize its impact and ensure a homogeneous level of information.
Finally, thanking the teams allows us to recognize their investment and thank them for the work accomplished.
Project Review: Reusable Template
Here's an example of a project balance sheet structure. You can use it as a template to write the project report tailored to your company's needs.
- The context of the project
- Gap analysis
- Risk management analysis
- Resource analysis
- Analysis of deadlines
- The technical assessment
- The methodological assessment
- The level of satisfaction of the sponsor
- Lessons learned
- The project manager's general summary
- The Conclusion

You can choose the most suitable profiles according to their relevance, expected margins or occupation rates in order to maximize profitability.
Writing a project report allows essential feedback, and helps to protect you administratively by confirming the successful acceptance of the project, thus closing it definitively.
However, to be relevant, the project assessment must be done cold, in a context open to discussion. Thus, it will help identify valuable lessons to improve the performance of your projects as well as the profitability of your company. Based on continuous learning, the project assessment is part of a long-term vision.
Questions:
There are different types of project reports.
- The progress report : during the project, it allows you to track deadlines, costs and the proper delivery of deliverables. It allows you to quickly identify friction and take proactive measures.
- The project review : at the end of the project, it helps to analyse gaps, draw lessons and capitalise on good practices.
- The production report: it intervenes on a regular basis according to the necessary rhythm and allows the activity to be monitored over a specific period.
Feedback (REX): more oriented towards continuous improvement and good practices, the latter is sometimes integrated into the project report.
The project report provides a complete overview of the project (objectives, schedule, budget, deliverables, results) and evaluates its overall success.
The REX project focuses on lessons learned: what worked well or badly, areas for improvement and practices to be replicated. The REX has a more qualitative and transversal purpose.
Here are the most used tools to carry out an end-of-project review:
- spreadsheets (Excel, Google Sheets) to structure the data,
- collaborative tools (Notion, Miro, Klaxoon) to lead the REX workshops,
- project management tools (such as Stafiz) to extract reliable data on times, costs, tasks and track progress throughout projects.
- Balance sheet templates or checklists so that you don't forget anything in the analysis.