What is the role of management control in companies?
Running a business without management control would be like driving a car without a dashboard: without knowing your speed, if you have any fuel left, or if your engine is overheating.
Thus, management control is essential to verify that the company is in good health and on track to achieve its strategic objectives.
In this article, we study the role of management control to help you understand its challenges and implement it effectively.
What is project controlling?
Definition
-
Measuring, analyzing, regulating
Project management control, also known in English as project management control or project controls, consists of measuring, analysing and regulating the performance and profitability of a company.
-
A cross-functional activity with a significant impact
Often associated with financial control, management control is in fact transversal because it concerns all aspects of the company. While it takes different forms depending on the size of the organization, it is always a condition for its success. It directs activities to achieve strategic objectives.
What is the purpose of management control?
-
Determining profitability
Management control analyzes activities in order to identify any discrepancies between the forecast and the actual, as well as their causes. This provides information on the profitability of the activity, among other things.
-
Identify the necessary adjustments
In addition, management control makes it possible to determine whether the achievement of objectives is still possible or whether adjustments need to be made. Thus, it makes it possible to redress the situation by proposing solutions.
Management control takes several forms, which respond to different challenges.
-
Budget management control to monitor financial performance
This stage of management control focuses on the evolution of financial performance. It involves budget planning, which helps to establish realistic budgets, aligned with the company's long-term strategic goals.
-
Strategic management control to align costs and objectives
This dimension is complementary to the first. Instead, it pays particular attention to aligning costs with strategic objectives in order to facilitate decision-making.
-
Operational management control to improve productivity
Management control from an operational point of view concerns productivity and in particular the optimization of resources. As a result, it is necessary to draw up an inventory of the areas that represent successes and those that are more critical. This will help identify potential optimizations leading to a gain in productivity.
Differentiating between audit and management control
The management controller, the person in charge of management control, generally has in his first missions the carrying out of audits.
The two activities are therefore closely linked. However, we differentiate between audit and management control because the latter not only offers a vision, but also offers concrete optimization solutions. Finally, management control is guided by the achievement of strategic objectives.
What are the challenges of management control?
Facilitate decision-making
Management control concerns all sizes of companies: groups, SMEs, startups, etc. because it helps guide decision-making . Analyzing results and producing reports for management, it provides material for:
- Identify the risks associated with current management
- Propose corrective solutions
- Recommend a strategy
This reliable and actionable data allows management to guide their decision-making and improve their working methods.
Establish processes to maximize financial performance
Management control controls, but also serves development. Thus, it allows you to implement processes to improve financial performance.
This involves:
- Implementation of monitoring methods
- Anticipating risks in order to reduce them
- Definition of financial strategies and budget forecasts
- Implementing corrective measures
Other activities help to improve financial performance, such as detecting budget deviations or reducing discrepancies between forecasts and actual expenditures.
Maximize productivity
-
Allocate resources optimally
Improving the Management of the resource planning and its planning is another challenge of management control. Indeed, it
helps to allocate resources in an optimal way, whether human, material or financial.
-
Maximize productivity
As with project management , this implies limiting underload and overload, which would have a direct impact on productivity and therefore profitability.
Thus, the management of the resource planning Distributes resources to ensure performance. She supports managers in their operational management and managers in their strategic management.
What are the main management control tools?
ERPs to consolidate data
An ERP is essential for management control activities. Indeed, it facilitates the management of the activity because it centralizes the data in the same place.
These data, generally collected in real time as with Stafiz, then become accessible and reliable, facilitating reporting tasks.
Budget management software for planning
Budget management software is also a key tool for management control. These are used to establish provisional budgets but also to monitor the budget directly. This type of tool facilitates the projection of sales and turnover and makes it possible to anticipate expenses in order to optimize them.
Dashboards to present data
Dashboards are the most widely used tools for management control. Indeed, thanks to data visualization, they present the company's performance in visual form and in real time thanks to the various key indicators chosen.
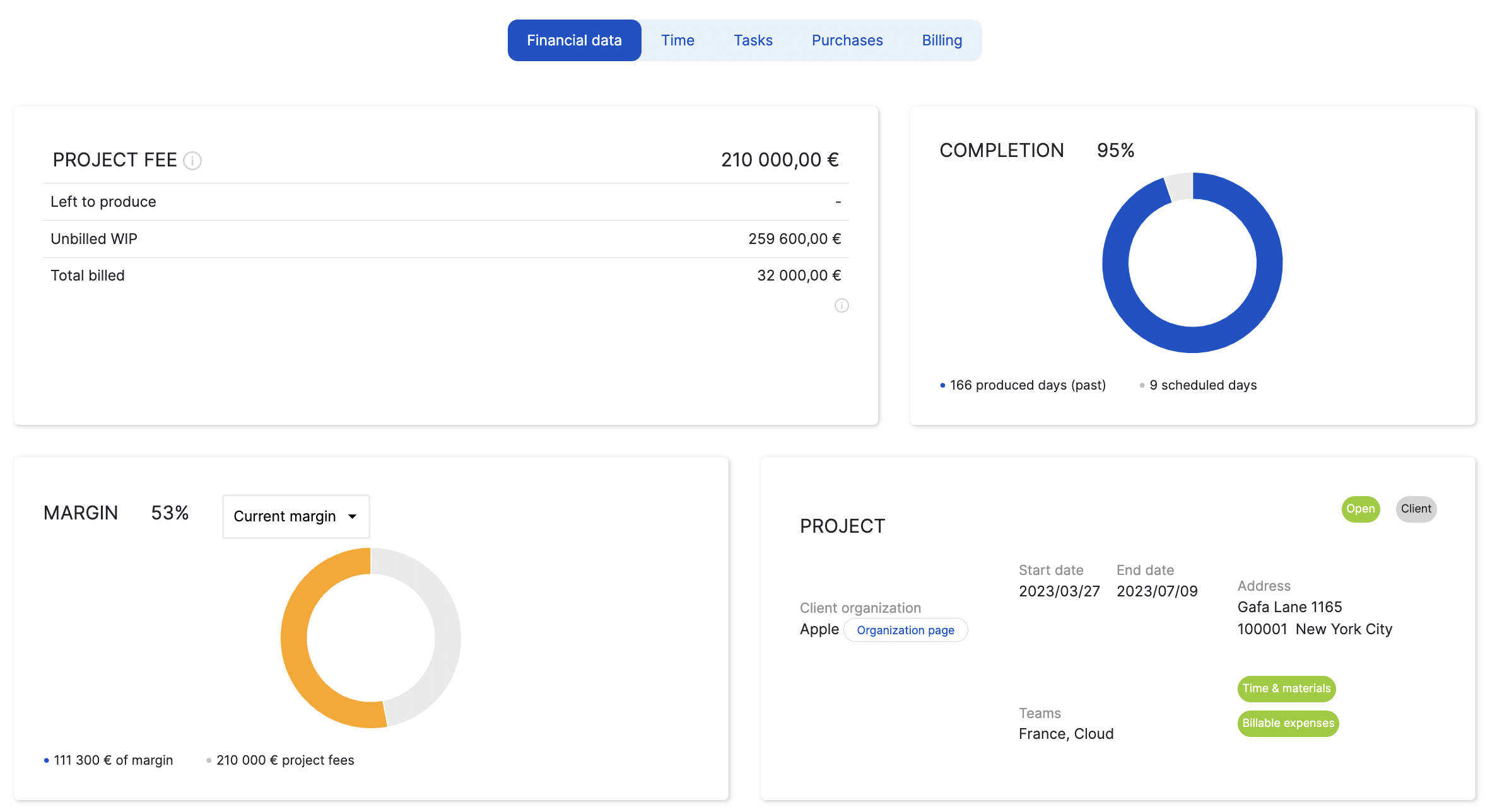
Reporting and statistics to share data
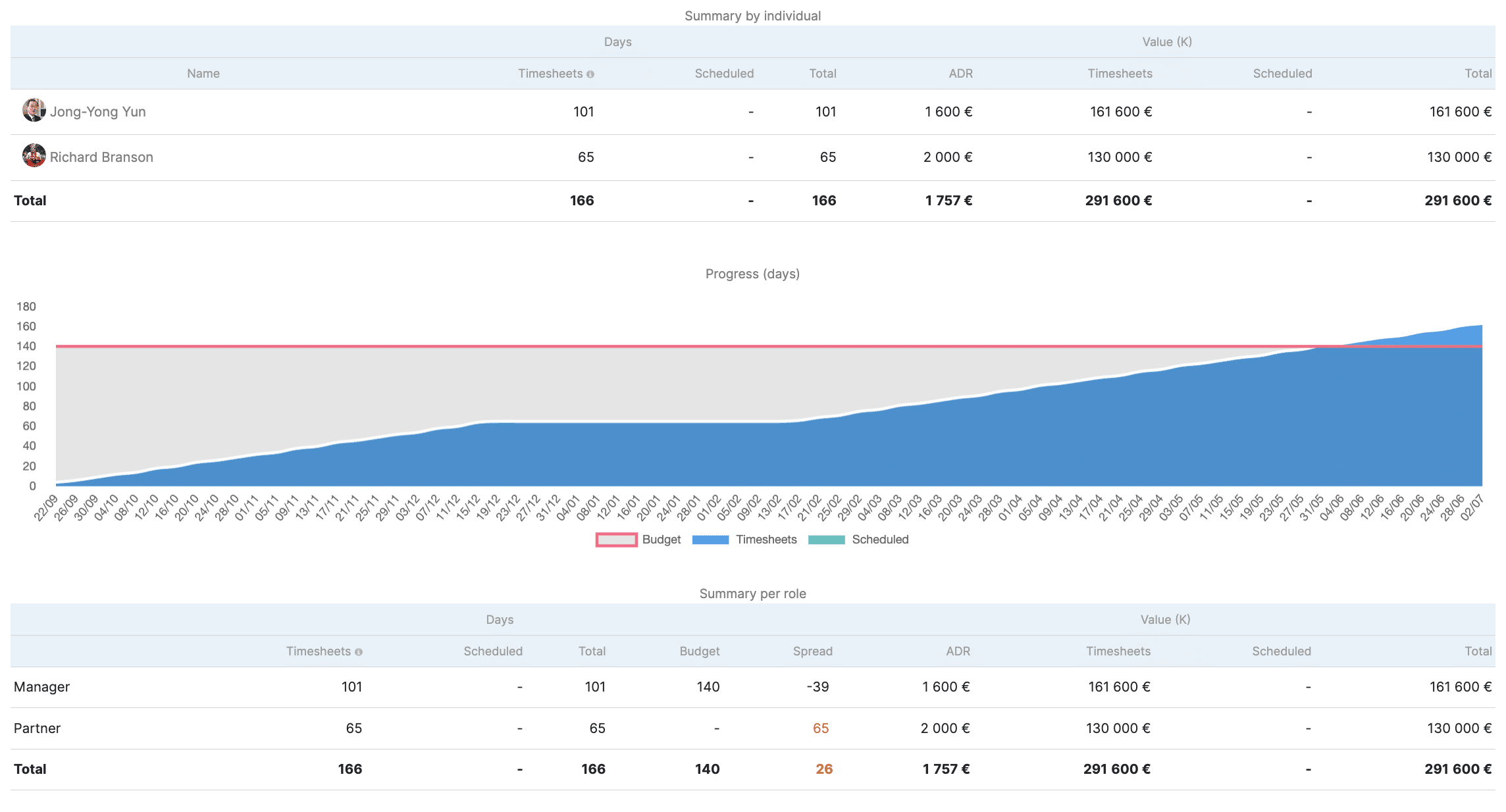
Reports also make it easier to visualize the company's performance , such as the mission report in Stafiz. The latter makes it possible to visualize the gap between the planned and the actual or to analyze the performance by employee and by team.
How to set up management control?
What are the steps of project management control?
Planning
The implementation of management control requires defining objectives and affirming a long-term strategy .
At this stage, you must also ensure the reliability and efficiency of the existing information system as well as its possibilities.
The latter must be able to report and collect information to be able to support the defined strategy.
Budgeting
The definition of the budget is essential in management control. This involves:
-
- Identify the company's resources
- Understand the constraints related to the activity and its market
- Define realistic scenarios based on the company's strengths and weaknesses
You can use budget management tools to define the provisional budget.
Taking action
Once your objectives have been defined, your budget identified and your strategy decided, it is necessary to put each step into action by calling on an experienced management controller.
The latter must know the company and its sector well in order to have the necessary hindsight to analyze and propose relevant recommendations .
Aftercare
Monitoring is one of the most important missions of the management controller. The latter monitors developments and analyzes the results, assisted by tools such as reporting and dashboards, present in particular in all-in-one solutions such as Stafiz.
Corrective actions
Finally, management control requires the provision and implementation of corrective measures in response to the observations observed.
Management control takes into account the audit of the existing situation but above all the passage to action that will make it possible to rectify the situation and achieve the defined strategic objectives.
💡 For all these steps, you can use budget tracking software such as Stafiz
What are the management control methodologies?
The methods of management control are varied, they can be combined. We recommend that you use the ones that are most relevant to your company, and that do not involve major internal reorganizations.
- Past and projected budget control
Actual and projected budgets are widespread management control tools.
This method consists of identifying and studying the discrepancies in order to make corrections. Projects must achieve expected results, on time and on time.
⚒️ Recommended tools: Dashboards, budget management software, Excel spreadsheets.
In Stafiz, the monitoring of these budgets is done at two levels:
- Project level
- Global level
At the project level, your teams can view this data in a consolidated way or over time.
The consolidated view allows you to observe the overall gap between the planned expenses (see screenshot below: "production plan") and the expenses that have been or will be made in order to complete the project (in the image: "current situation at completion").
The view through time or "timeline" allows you to have more precision on the discrepancies by identifying when the budget overrun would take place and especially for what reasons it would occur, thus avoiding it.

- Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
This method, in English "Activity-Based Costing (ABC)", consists of analyzing the costs per activity in order to determine the profitability of the different operations.
The objective is to identify the most resource-consuming activities in order to adjust
processes and efficiency.
⚒️ Recommended tools: specialized ABC and ERP software
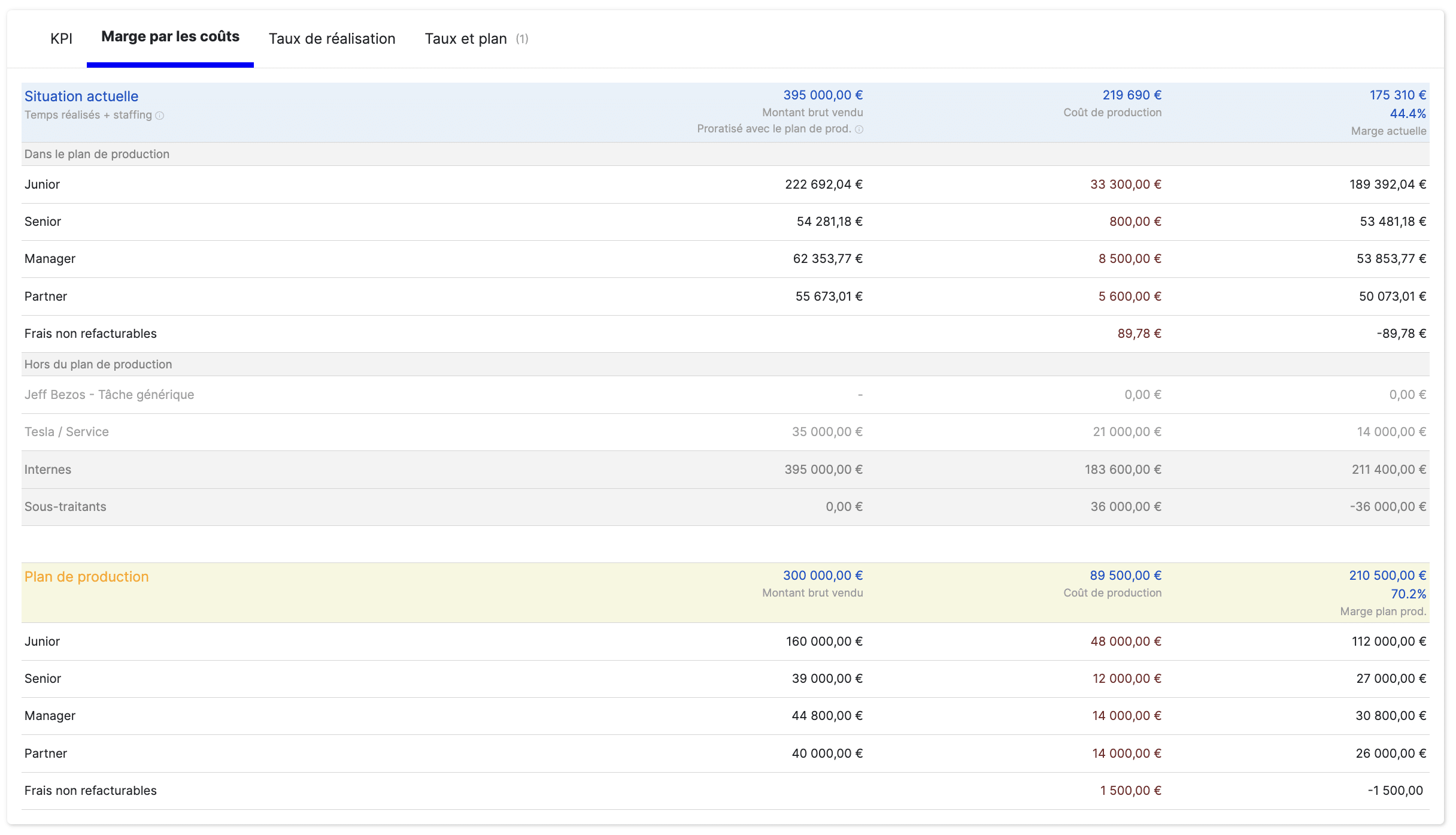
Stafiz offers you the possibility to analyse your activity by activity (BU, region, etc.). You can compare your activities, identify the most and least profitable ones...
Another angle of analysis is the distribution of turnover between different teams and poles in order to understand the interest and participation of each team:
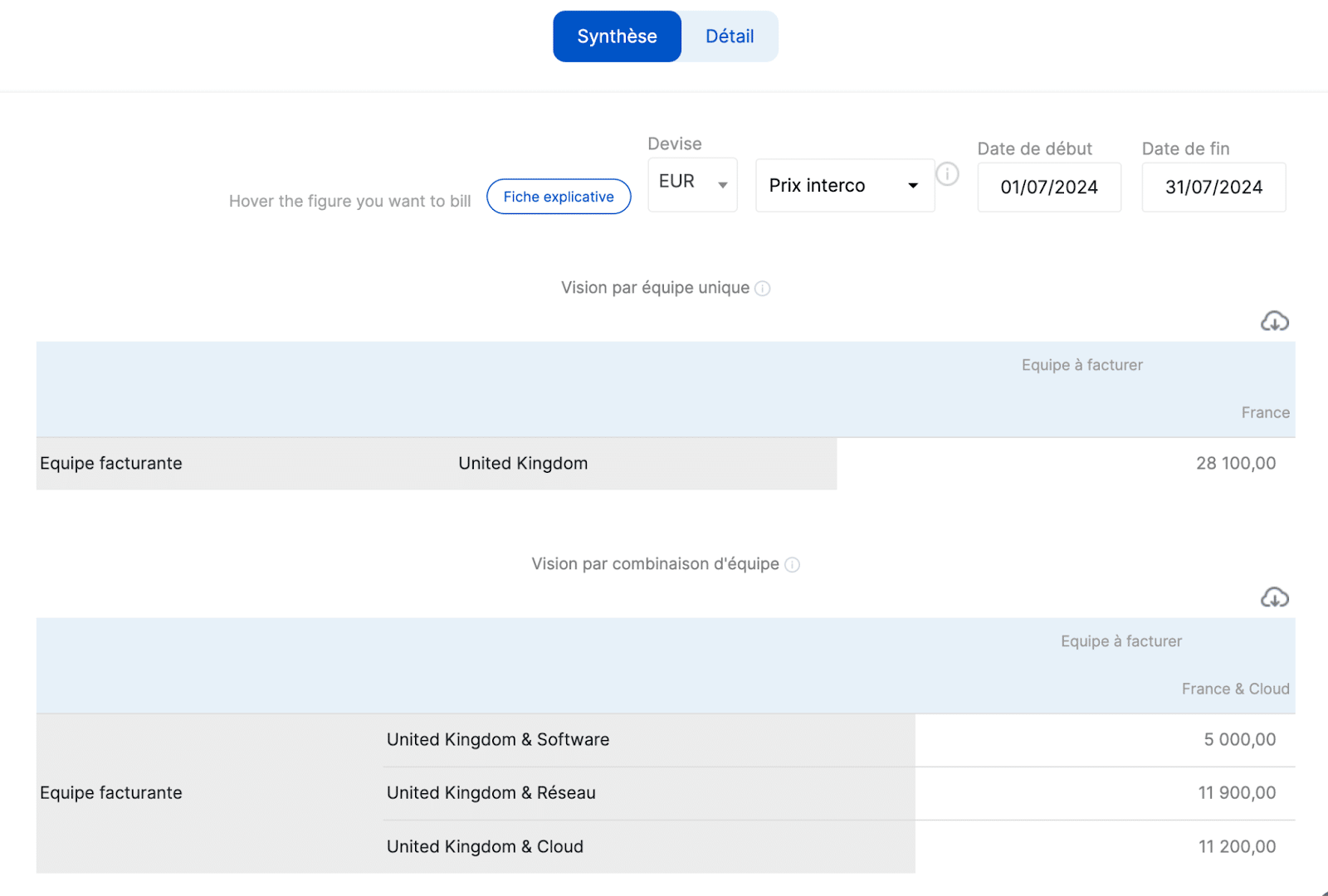
- Management by Objectives (MBO)
Management by Objectives (MBO) sets specific objectives and evaluates performance against them. In this way, the teams' efforts are aligned with the company's strategic objectives.
⚒️ Recommended tools: Balanced scorecard and performance management systems, allowing you to visualize goals against reality.
Management by objectives is the cornerstone of Stafiz.
Various indicators will allow you to measure your performance against objectives. Let's explore two of them:
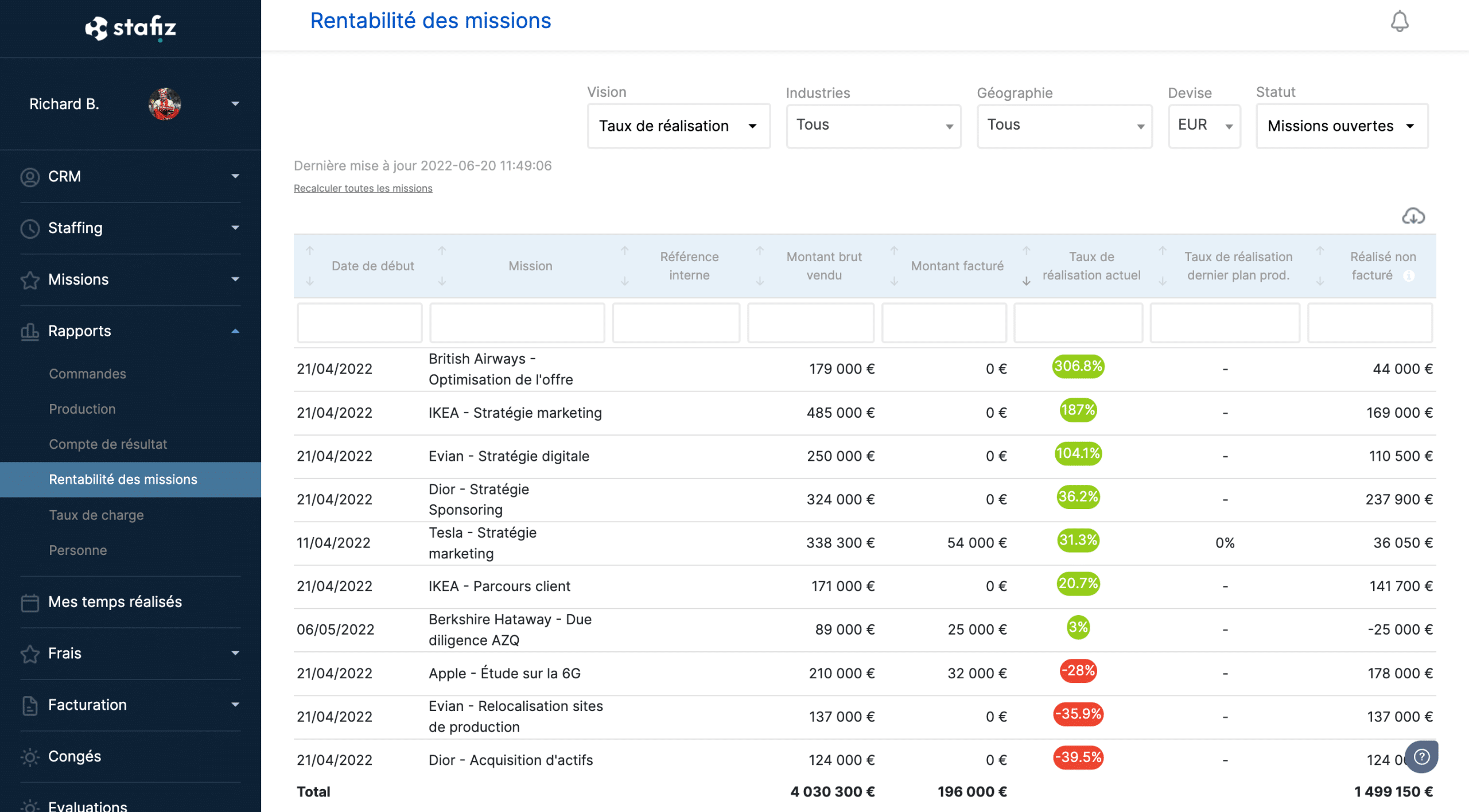
1. The rate of achievement of the objective
The completion rate is a great indicator to understand in a single number whether a fixed-price mission is profitable or not. This is the ratio of:
amount sold / what I produced (or "how much I should have sold")
A normal completion rate is 0%. This means that:
- If your current rate is -10%, you are 10% less profitable on this mission than you hoped
- If your current rate is 20%, you are 20% more profitable on this mission than you hoped
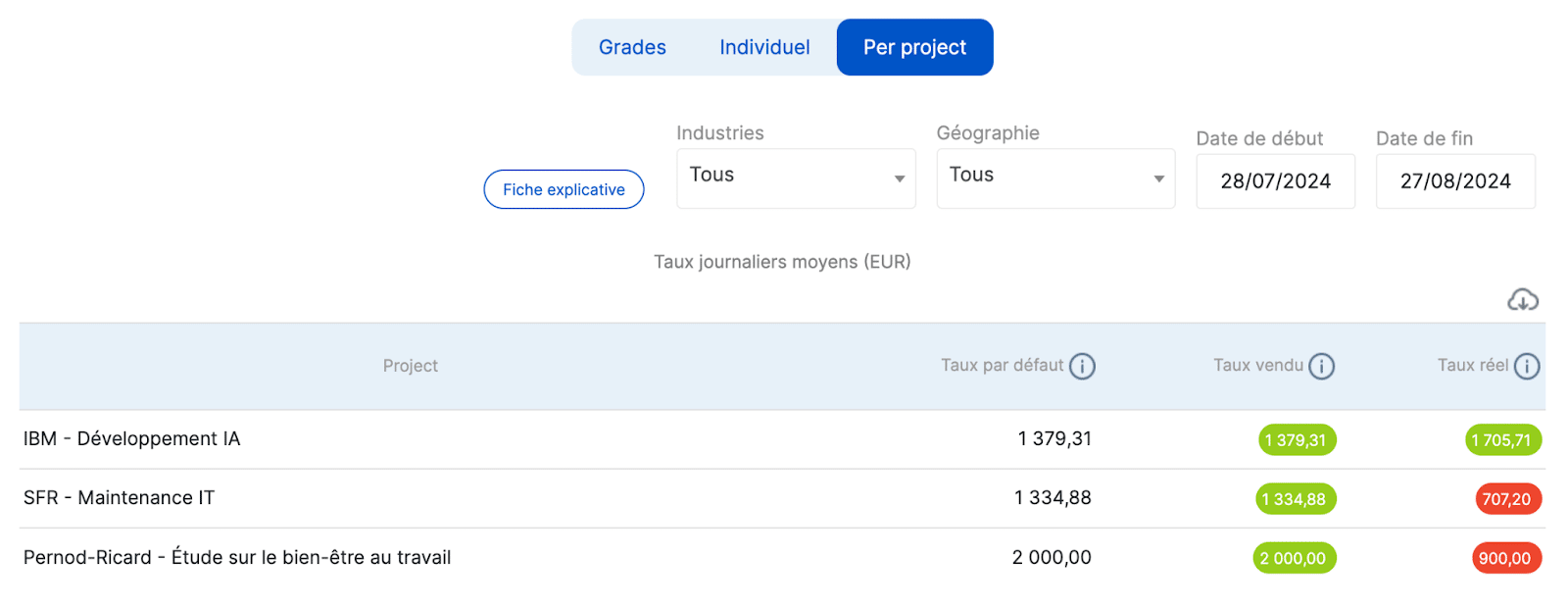
2. Analysis of ADRs sold vs. actual
This analysis allows us to observe the performance of projects through the prism of daily rates:
- If we work fewer days than planned on a project then the daily rate will be higher than the actual
- If we work more days than expected, the daily rate will be lower at the REE
- Financial Ratios
Financial Ratios uses ratios to assess the financial health of the company. The goal is to provide clear and measurable performance indicators to facilitate decision-making.
⚒️ Recommended tools: Financial dashboards and ratio analysis tools
- Management control by key performance indicators (KPIs)
KPI management control consists of monitoring key performance indicators specific to strategic objectives. This helps measure the efficiency and effectiveness of operations with the goal of improving performance.
⚒️ Recommended tools: KPI dashboards and other business intelligence software
- Integrated Performance Management
Integrated Performance Management involves integrating all aspects of performance into a single system. The objective is to offer a clear and global vision of performance.
⚒️ Recommended tools: Integrated ERP systems and other business performance management tools
This aspect is the great differentiator of Stafiz. Integrated business management, which goes beyond management control, includes various aspects:
-
- Operational with the monitoring of tasks and phases and therefore of progress to meet deadlines
- Financial: with variance analysis, financial objectives (revenues, costs and margins)
- Strategic: the consolidated view of this data, particularly financial, provides a past but also a forecast view of the activity
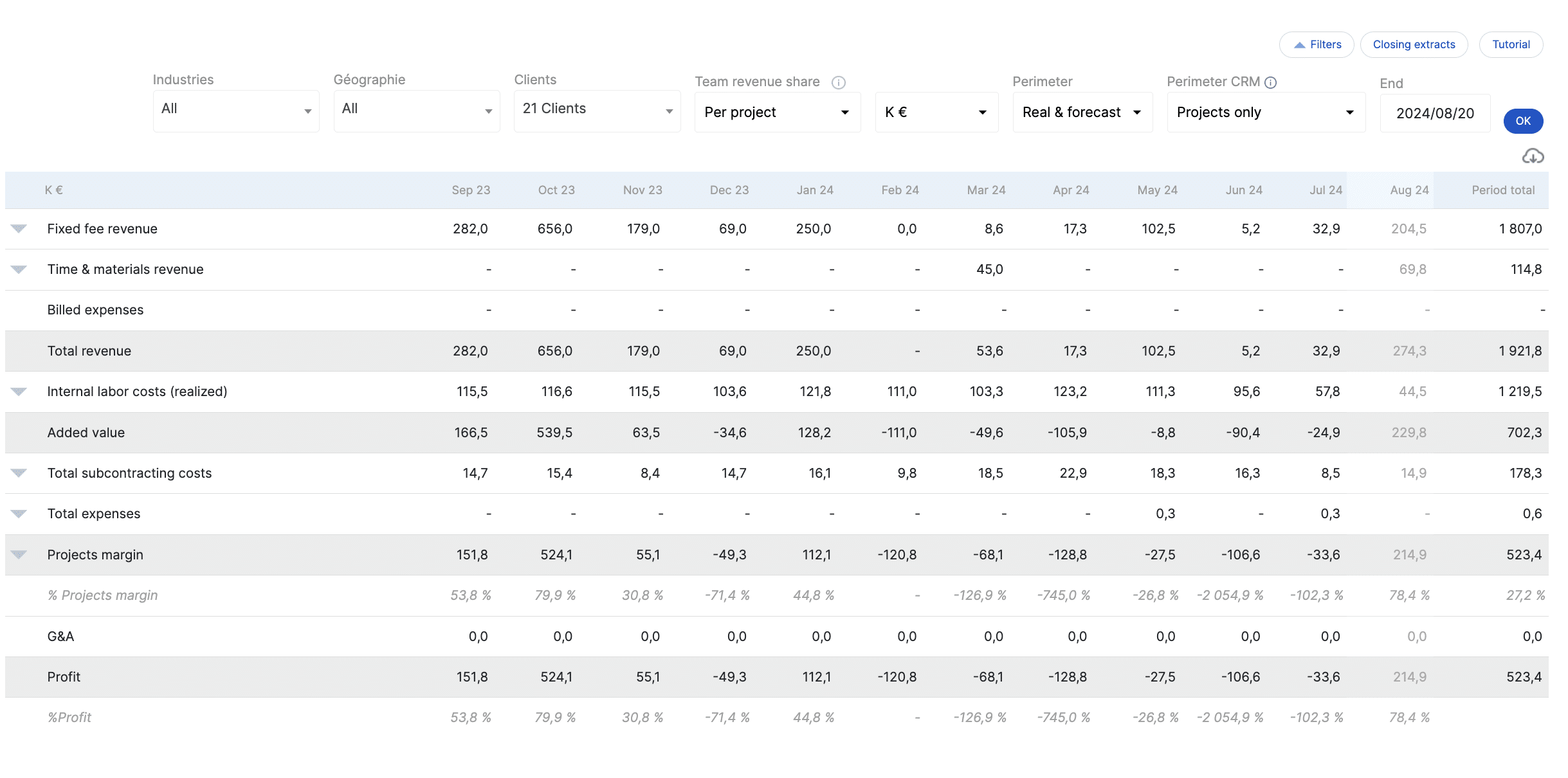
- Agile Management Control
Agile management control reuses agile methods to quickly adjust processes to change needs. This requires a high degree of flexibility and seamless collaboration made possible by continuous measurements. This version of management control is more dynamic in the short term.
The objective is to improve the responsiveness and flexibility of the organization in the face of unforeseen events.
⚒️ Recommended tools: Agile management software, combined with Scrum and Kanban methodologies.
What are the KPIs to track for management control?
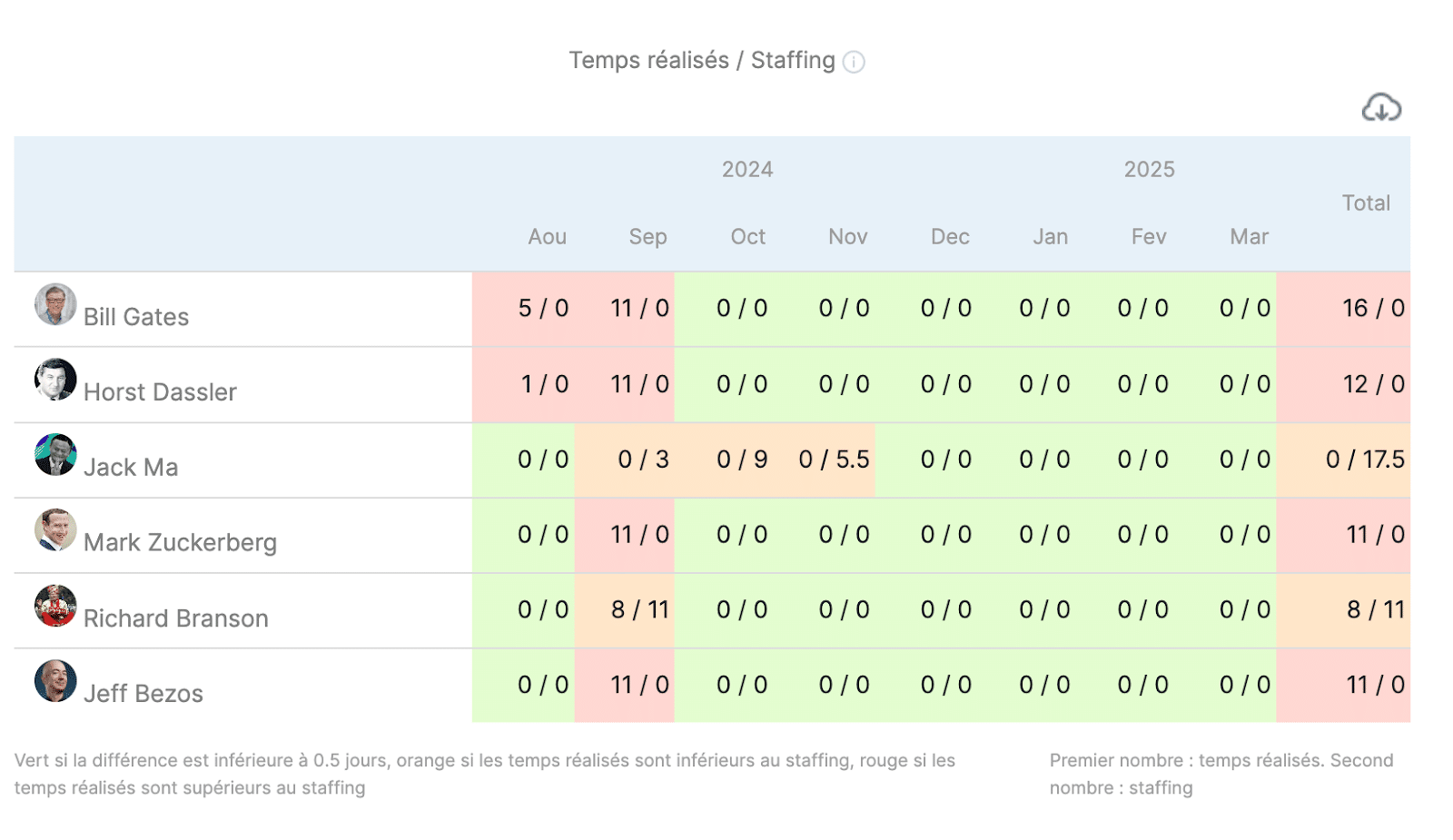
- Cost Variance
Comparing actual costs with budgeted costs helps identify variances. This helps monitor budget overruns and take corrective action.
In Stafiz, you have a view of the variances in days and therefore in valuation by project or all projects:
- Actual vs. Projected Revenue Variance
Analyzing the discrepancies between actual and projected revenue helps adjust sales and marketing strategies by taking into account actual performance.
- Gross Margin
Gross margin is the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold. It is expressed as a percentage of turnover.
Gross margin is used to evaluate the gross profitability of products or services.
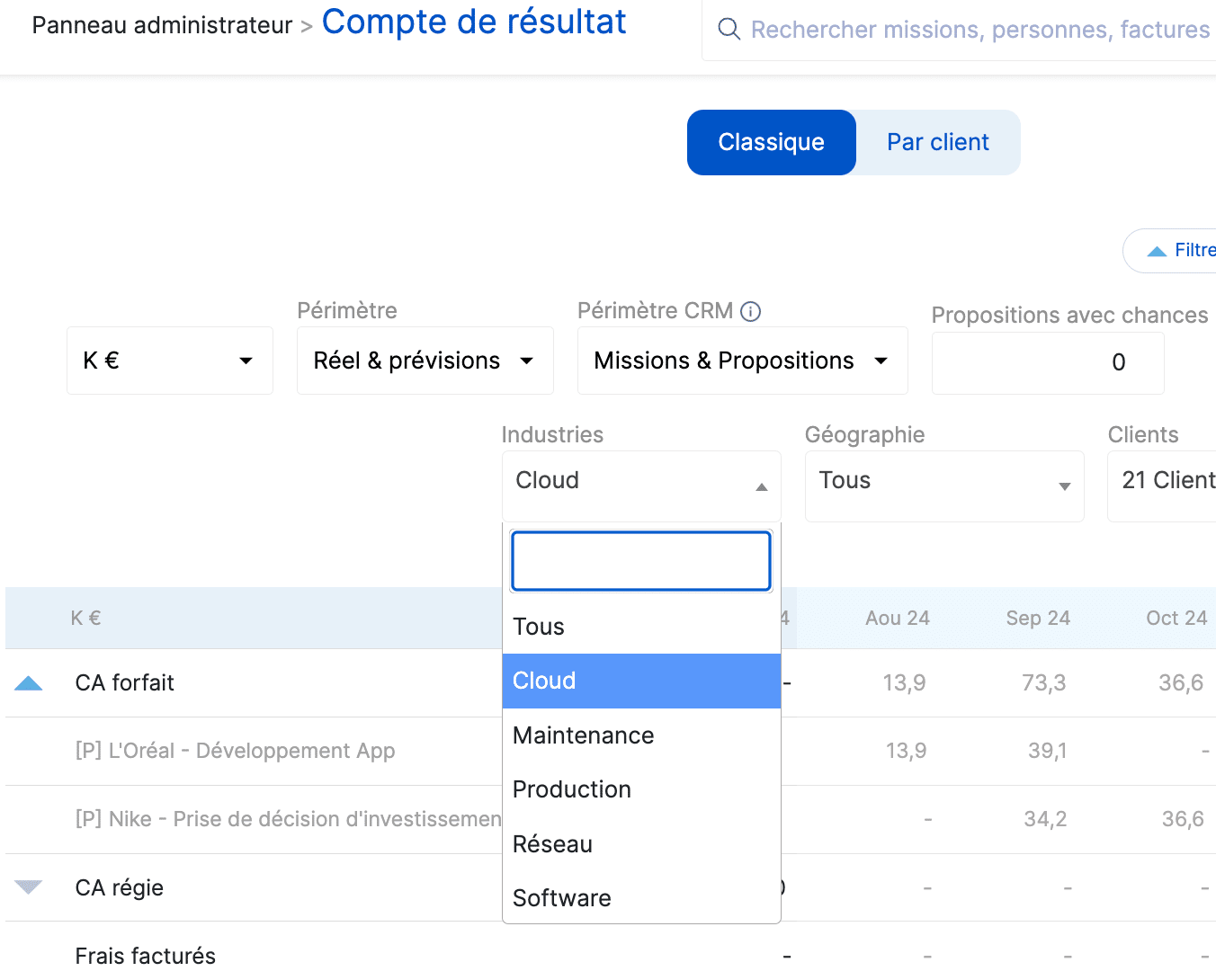
In Stafiz, the vision of the margin is both granular, by project or across the entire portfolio, and at different levels, after internal and external expenses or overheads:

Past and projected income statement with the various costs
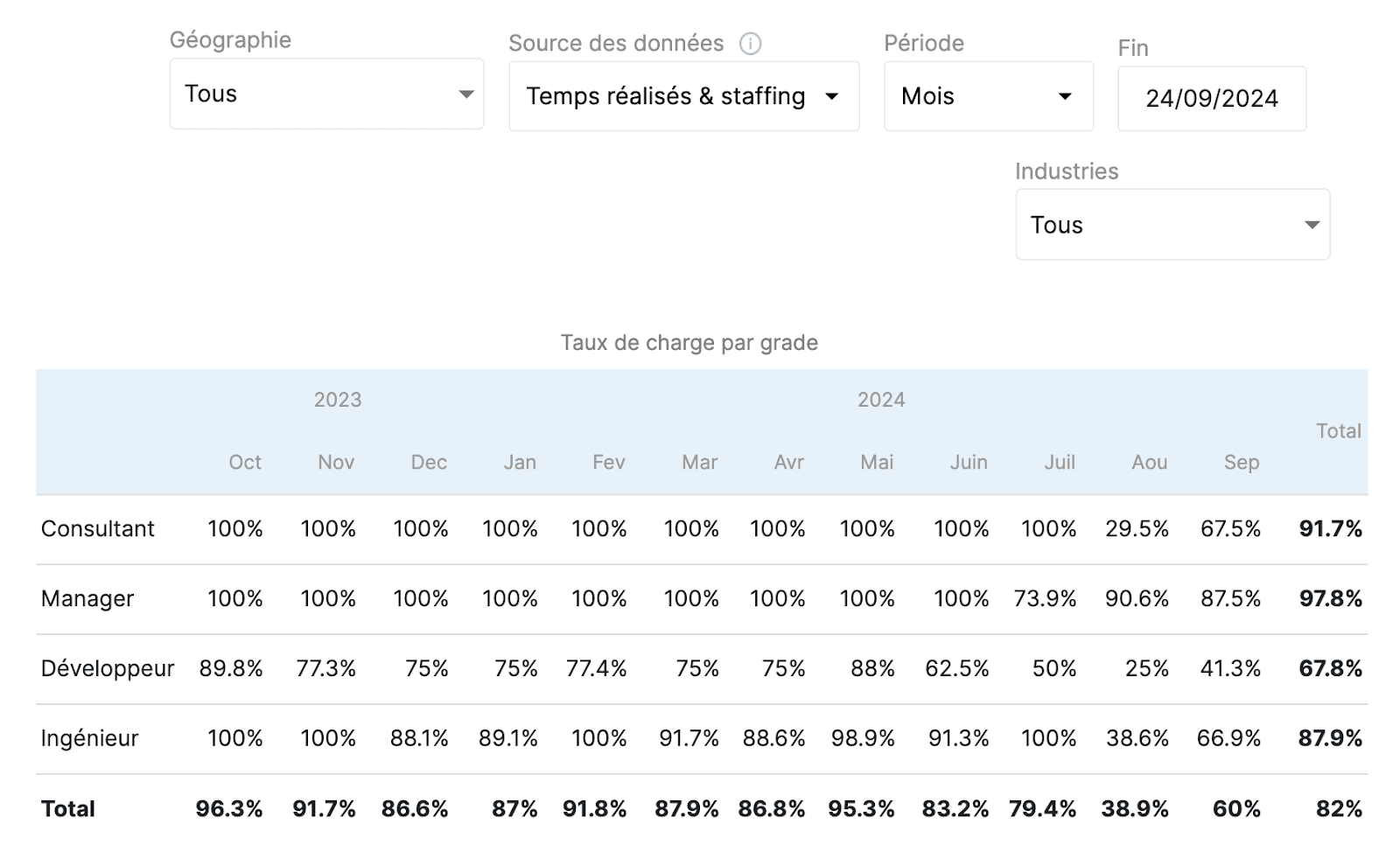
- billable utilization rate (utilization rate excluded leave)
The Activity Rate excluding leave calculates the number of days produced on the number of potentially billable days, i.e. the total number of days minus the days of leave and RTT.
The billable utilization rate is a relevant indicator for optimizing resources and thus improving operational efficiency.
In Stafiz, you can monitor your utilization rate with granularity and flexibility as well as predictive with dedicated reports.
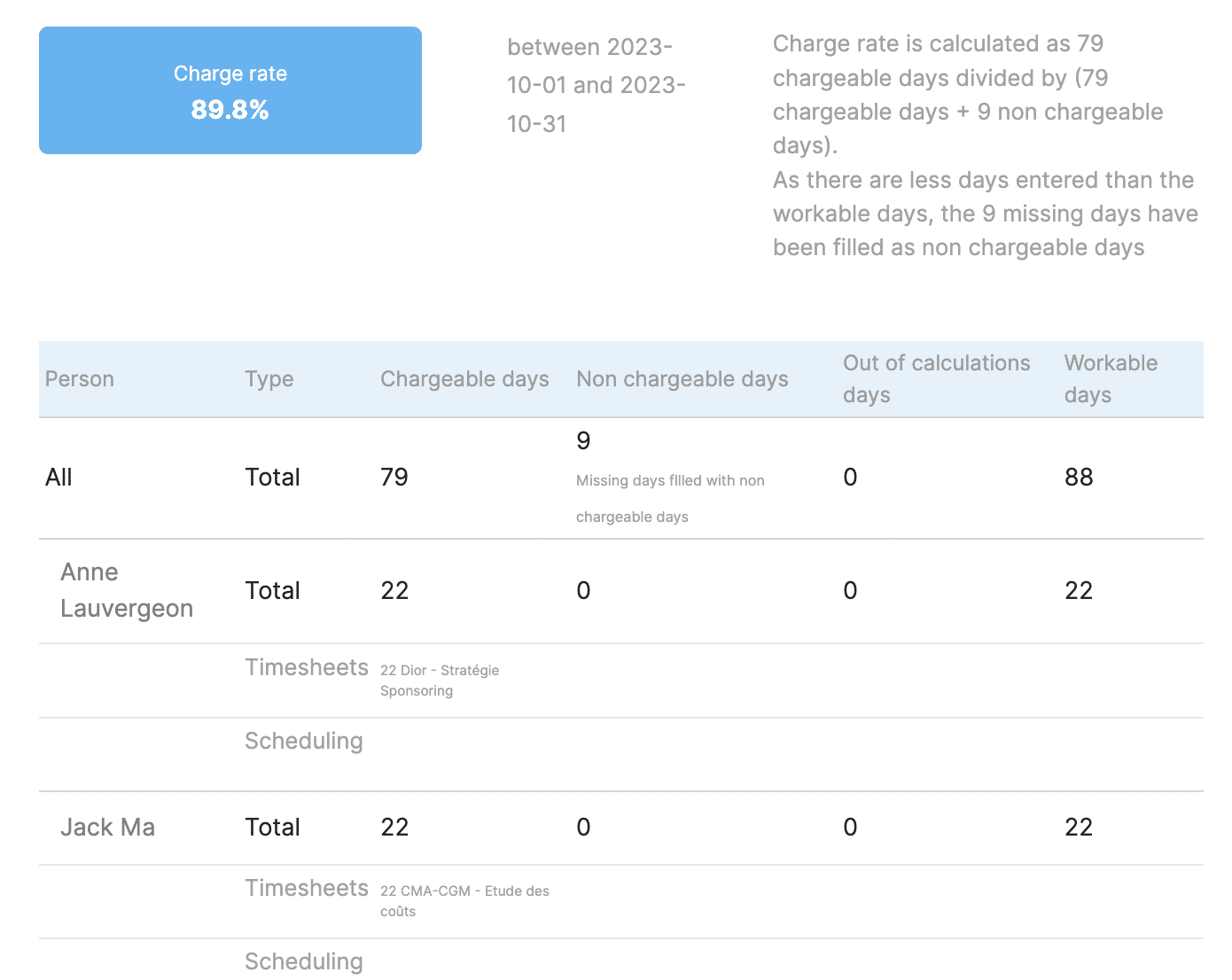
You can even zoom in on each of the rates to understand the rate in detail.
- Productivity per Employee (Not written: see email questions)
Description : Revenue or profits generated by employees.
Objective : To measure the effectiveness of the workforce and identify opportunities for improvement.
How to analyze the results of project control?
Compare performance
To be meaningful and interesting, the audit of management control must be analyzed. A first step is to compare the performance:
-
-
- Between the actual and the forecast
- At the global industry level
- Compared to past projects
-
The objective is to observe the gaps and dig deeper to understand the causes.
Studying performance criteria
For each project, it is essential to determine evaluation criteria. These can vary depending on the objectives of the project or the company as a whole. Often, the quality of the deliverable, the respect of deadlines and costs are used as criteria.
This indicator provides an overview and allows you to analyse the adherence to project deadlines.
Take corrective action
-
-
-
Root cause analysis
-
-
Also called Root Cause Analysis – RCA, this method is used to determine the origin of a problem in order to correct its consequences. It requires clearly identifying the problem and gathering information to limit its consequences. It can pass
Through exchanges with the teams, careful observation, or with the 5 whys technique.
Questions:
- Establish clear and measurable objectives;
- Budget for necessary resources;
- Use powerful monitoring and reporting tools;
- Implement proactive risk management;
- Optimize communication and collaboration;
- Continuously evaluate and adjust performance.
The dashboard is a tool used in management control to visually represent the progress of objectives.
For greater efficiency, management control dashboards are most often computerized, in order to process data automatically, generate reports, and store the history of it.
- Monitor the progress of objectives in real time;
- Facilitate communication between the various stakeholders;
- Anticipate risks to better prevent deviations;
- Set up a specific follow-up on corrective actions.