How to Measure Project Profit?
In a professional services sales business, it is very important to track the profitability of projects. This indicator is crucial for growing your company, and ensuring that the business as a whole is profitable. Service companies that sell projects need to be able to track thesustainability of each project in order to be able to make the right decisions. Here we explain how to calculate the profitability of a project.
How to Measure a Project's Revenue?
Theoretically, turnover is recognised when ownership of an asset is transferred or when the service is fully performed.
However, in the context of projects that can last several months or even years, it is possible to apply another methodology to recognize turnover as the project progresses.
The choice of methodologies applicable in your case must be validated by your accountant or auditors.
The calculation of a project's turnover must comply with the accounting principles in force. There are several approaches to recognizing turnover, which requires a good knowledge of the financial indicators used in project monitoring.
Recognition of revenue vs. billing
In this approach, turnover is recognised on the basis of the amounts invoiced during the period, made possible by precise time tracking. Billing = Revenue.
This is generally the method applied for projects under direct management (invoiced by time spent).
Your recorded times are automatically converted into invoices.
Progress-Based Revenue Recognition
At the end of each accounting period, a project progress rate is calculated (this rate must also comply with an accepted accounting methodology).
The turnover recognised over the period corresponds to the amount sold multiplied by the rate of progress, from which the amount of turnover recognised over the previous period is deducted.
This is a method often applied to fixed-price projects.
Completion Revenue Recognition
For short projects, invoicing on completion is the most common methodology. In this approach, revenue is recognized when the project is completed. To ratify this closure, the client often signs a report of completion or another document justifying that the service has been provided.
Stafiz is an ERP for professional services and service companies. Learn how to better manage your projects, track their progress, and increase margins.
Once your turnover has been calculated, you can then determine the profitability of a project.
How to Measure Project Profit?
Formula for calculating the profitability of a project
To calculate the profitability of your project, simply subtract all the costs of the project from the turnover it generated.
Profitability = Turnover – Costs
In order to get an accurate and reliable result, make sure you have all the necessary visibility into the project's expenses. This is all the more important for your budget monitoring process throughout the project : costs must systematically be reported and taken into account in real time.
Project Profit: Which Costs Should Be Taken into Account?
All project costs that have been defined in the budget must be tracked, otherwise the scope of analysis is different between the budget and the realized.
So here are the costs that need to be tracked, and the best way to do it.
- Employee time costs: A project management tool or ERP for your service company allows you to track the time spent on project tasks and assign associated costs to each employee based on their salaries.
- Subcontracting purchases : you must take into account the costs of subcontracting on the project, either through subcontracting invoices or again through the ERP for your service company. Such software allows you to track subcontracting, whether it is related to the time spent by a freelancer, or whether it is billed to you at a fixed rate.
Track your external employees' performance
In Stafiz, your externals are included to collaborate directly from the platform through specific accesses. Time entry is simplified, and their invoices can be shared directly with you.
- Non-rebillable expenses and other purchases : You should include the costs associated with this project, such as travel, catering, IT license purchases, etc., in the business case . As soon as the costs are not re-billable on an actual basis, they will have an impact on the margin and must therefore be taken into account
How to analyze the profitability of a project?
Knowing the profitability of a project is particularly important in a professional services business. Consulting firms, agencies, and all activities that sell projects must follow the margins of their projects.
This profitability indicator makes it possible to understand the possible reasons that penalise the profitability of the activity as a whole, and limit growth.
It is necessary to analyze the profitability of projects from several angles.
Compare profitability between different types of projects
It is necessary to be able to analyse the difference in profitability between projects sold on a fixed-price basis and projects sold on a time-spent basis (under direct management).
Generally, time-based projects are less risky from the point of view of profitability since a selling price by the hour or by the day is determined and this must theoretically already include a margin. However, sometimes not every day is billed or fees penalize the margin.
Margin tracking is even more important for fixed-price projects. In this type of project, the sale amount of the project is fixed in advance and is not supposed to change. If the work to complete the project is underestimated, there is a risk of cost overruns. Conversely, by optimizing the time spent on the project compared to what was sold, it is possible to make a much higher margin.
The profitability of projects according to the teams
You need to be able to group projects and group them according to the angles of analysis that may interest you: by team, by sector, by business unit.
All that is needed is for each project to have a "tag" to indicate which team, sector, business unit it is linked to in order to then be able to consolidate the data.
Compare profitability to the initial budget
The profitability of a project is compared to other projects, but also compared to the initially planned budget.
Creating a project budget at the start of the project is a key step in being able to monitor and improve performance. It is the measurement standard that makes it possible, during the course of the project, to know whether we are deviating or whether the project is at risk.
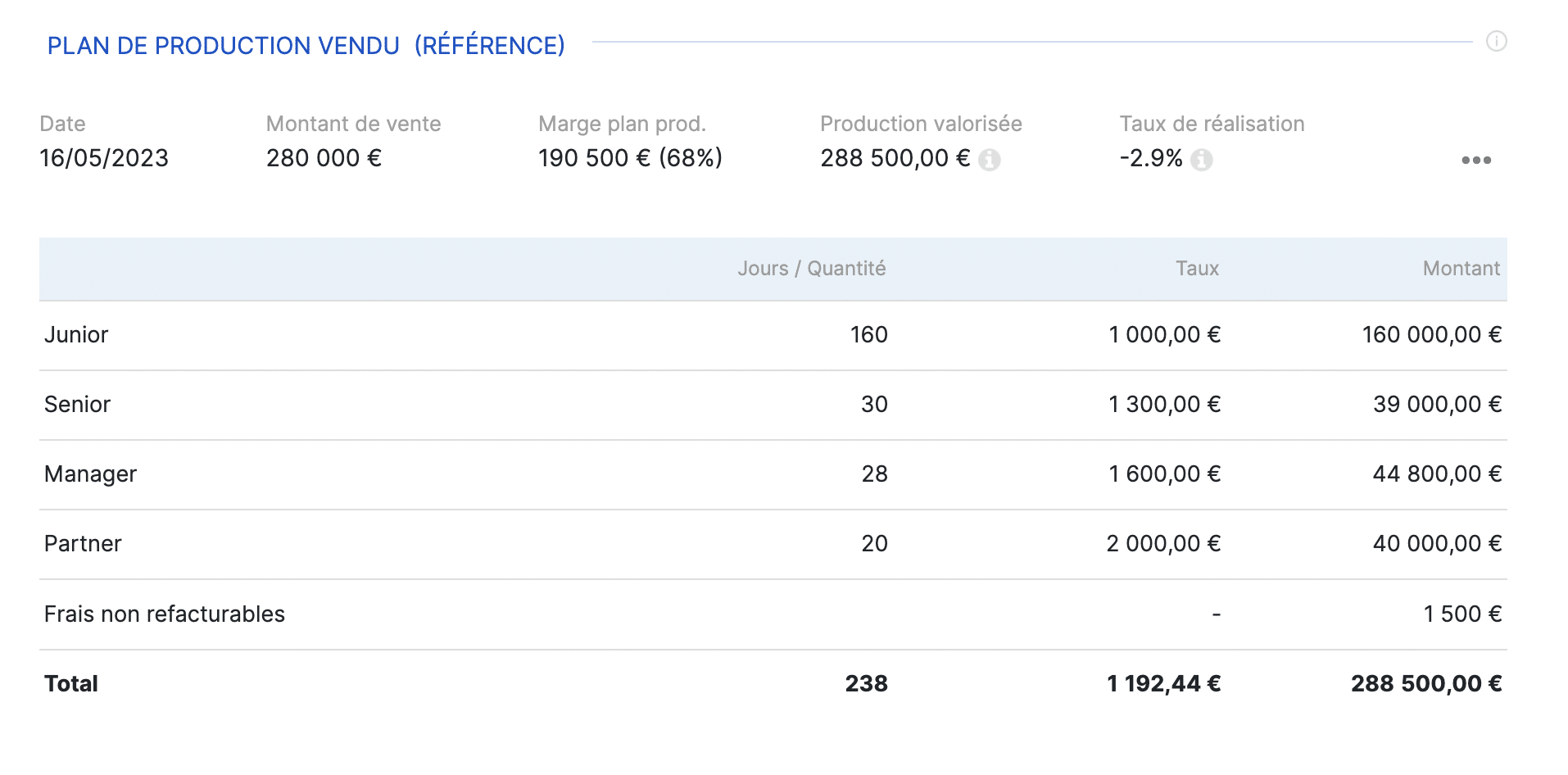
To build the budget for a project, it is necessary to estimate the following:
- the time that employees will have to spend on the various tasks of the project;
- the cost associated with this time spent by employees;
- subcontracting purchases when there are any on the project;
- the costs that will have an impact on the margin (those that are not rebillable on the actual basis of the project);
- any purchases of products, which are then used or resold as part of the project. For example, software licenses.
With all these elements, it is possible to calculate the set of expected costs for the project.
These costs are deducted from the projected project turnover, which makes it possible to calculate the projected project margin.
Not using a project accounting software yet? Find out their benefits and why you need them.
What are the profitability indicators of a project?
Project gross margin
A key indicator for the CFO or CFO, the gross margin helps to detect anomalies in a project, such as under-invoicing or a lack of framing.
Formula: Invoiced Revenue – Cost of Production (Internal + External)
The margin rate
This indicator allows you to compare several projects with each other, and identify which mission or type of project is the most profitable. From a strategic point of view, it helps guide future business decisions.
A rate above 20% generally signals a problem with project management, or even pricing.
Formula: (Gross Margin / Project Revenue) × 100
The utilization rate Sold
This is a key indicator for service sales businesses such as agencies, IT Services or consulting firms. The utilization rate Sold makes it possible to detect losses related to unproductive time that is not invoiced, such as meetings or revisions.
Formula: Billable Hours / Total Hours Spent on the Project
The average hourly cost per profile
This is the actual average cost of a consultant per hour, taking into account:
- his salary,
- the associated expenses,
- indirect costs.
Compared to ADR Initially sold and invoiced to the customer, it reveals the gross profitability of the resources mobilized.
Stafiz helps professional services gain visibility and better manage their project progress thanks to real-time data, the consideration of all costs and financial KPIs. Stafiz is a SaaS for managing the resource planning, project management and Business Intelligence. This way, budgets and margins are always respected and you make better decisions for your business.
To learn more about the Stafiz platform, request a demo.
Questions:
The break-even point is the level of revenue needed to cover all of a project's fixed and variable costs. Below that, the project generates losses; beyond that, it becomes profitable. It therefore makes it possible to define the volume of activity or invoicing at which a project begins to create value.
The NPV (Net Present Value) measures the value created by a project after discounting the financial flows. The IRR (Internal Rate of Return) indicates the expected rate of return, useful for comparing several projects. The Profitability Index expresses the ratio between present value and initial investment, which is useful for prioritizing projects when there is a budget constraint.
Cost per job helps control resource consumption per activity, avoiding unplanned overloads. The project margin (difference between revenues and total costs) directly measures financial performance. Finally, the cost variance compares the estimated budget and the actual costs, making it possible to quickly identify drifts and correct the management during the project.
The project profitability index measures the ratio between the present value of a project's future flows and its initial investment. It allows you to compare different projects in order to prioritize them according to the best potential ROI.
-
- If it is less than 1, the project is profitable.
- If it is equal to 1, it covers its costs but does not generate a profit.
- Above 1, the profitability index indicates a risk of financial losses.
A project is profitable when it brings a return on investment, whether financial, strategic or organizational. Monitoring of the right indicators (margin, utilization rate sold, planned/realized variances) then allows us to judge precisely.


