How to make a step-by-step project schedule
Project schedule is one of the pillars of project management.
Indeed, the latter gives direction to your project and offers a global vision, thus facilitating decision-making.
In addition, the project schedule provides transparency that stimulates the motivation of the teams and encourages the growth of the company.
However, the implementation of a project schedule cannot be improvised. To be effective, a project plan requires rigour, anticipation and taking a step back.
In this article, we present the 9 steps to make an effective project schedule.
Step 1: Prepare the project
Setting up a project schedule involves clarifying the objectives to be achieved.
This scoping phase helps to clarify expectations and ensure alignment of all stakeholders in order to get to the heart of the project.
Thus, the project schedule begins with a preparation phase where you will define how the project will be executed and controlled.
This scoping phase lays the foundations of the project and details:
- the various tasks;
- the phases and order of execution of the different activities;
- the human resources required
- budget and costs.
The framework note then makes it possible to keep the traceability of this context.
A real roadmap, it takes the form of a document that answers 5 essential questions.
- What: What does the project consist of? What needs to be done?
- Who: who is in charge of what?
- How: What are the tasks to be accomplished? What are the deliverables?
- When: on what time scale? What is the timetable?
Like the project progress report, it is intended to inform the teams.
Finally, the preparation phase represents an opportunity to anticipate needs.
Take the example of project management software Stafiz, which can help you estimate the resources you'll need before you've even started your project.
- Integrate CRM and project management tool
Indeed, Stafiz accepts many integrations.
You can then link your CRM and be alerted when the project has a high chance of being won to start preparing your resources.
- Forecasting recruitment and training needs
In addition, Stafiz offers a total capacity curve that shows the current and future load.
This feature provides a clear view of future requirements, enabling you to anticipate recruitment or training needs.
Step 2: Choose the right project schedule tool
Although it is possible to combine several tools (Gantt chart, PERT, etc.), using a single project schedule tool will allow you to centralize all the data, to gain reliability and flexibility.
Excel, the false good idea
Excel is not well suited to setting up and updating a project schedule. Indeed, the document quickly becomes complex to use and interpret.
Columns, merged cells... Any addition of information requires drastic formatting.
Excel was not designed to plan or manage projects.
Use project schedule software
Instead, we recommend using dedicated project planning software.
Indeed, this type of tool makes it possible to evolve the schedule and the different components of the project according to the hazards.
Thus, Stafiz is a complete tool designed to facilitate project management. It allows:
- centralization of data (reliability);
- real-time monitoring (responsiveness for better decision-making);
- the possibility of cross-referencing data;
- communication and information sharing (team productivity).
Step 3: List and prioritize tasks
List all milestones and tasks
This step consists of making an inventory of all the tasks that will have to be carried out during the project.
Milestones, tasks and sub-phases can be distinguished, from the broadest to the most precise.
- Milestones represent major stages in the process (e.g. sending specifications to the customer).
- The tasks represent all the elements that make up the project (e.g. drafting of the specifications).
- Subtasks are all the elements that make up the tasks (e.g. proofreading and correcting the document).
The more tasks are broken down the more visibility you have over the work to be delivered.
This will allow you to be as accurate as possible when you need to estimate the budget.
In addition, you will be able to build a more precise schedule in order to ensure your commitments to the customer.
To help you make a list of tasks, you can use the Project Breakdown Structure (WBS).
Identify dependencies
After identifying all the tasks that make up the project, you need to determine which tasks need to be done before others, and which ones can be done at the same time. To do this, identify the interdependencies between tasks so that you understand their impact and how best to prioritize them.
In the case of a bakery, it's impossible to make bread if the flour hasn't been purchased. In the case of a digital project, the sequences may be less clear, but they have just as much impact.
Indeed, if this step is neglected, it can jeopardize your schedule and your project.
Take into consideration the response and validation times of your employees and service providers.
Several tools exist to help you identify dependencies.
The PERT diagram organizes tasks in a network to provide an overall view of the project, as well as prioritized, parallel and critical tasks to meet deadlines.
The critical path is to break the project down into the longest sequence of tasks to complete the project.
Each task that affects the duration of the project is then reflected throughout the entire sequence.
This method allows you to obtain a pessimistic view of the project in order to organize the project schedule strategically.
Scheduling tasks
Once dependencies are identified, categorize tasks by considering:
- the outbuildings;
- priorities;
- the impact generated and the importance of each task.
Step 4: Set a budget
The schedule and budget are closely linked and must therefore be determined in parallel.
In reality, the project schedule must be built based on 3 components at once:
- the budget,
- resource selection,
- resource allocation.
Rely on the available elements
Gather all the information you need to build the budget : These include the list of tasks, dependencies, risk management and resource allocation, which we'll discuss in a later section.
The more information you have, the more realistic your budget can be.
Use a dedicated tool
Many tools dedicated to budgeting exist to help you in this step.
To establish a projected project budget, start by determining the feasibility of the project.
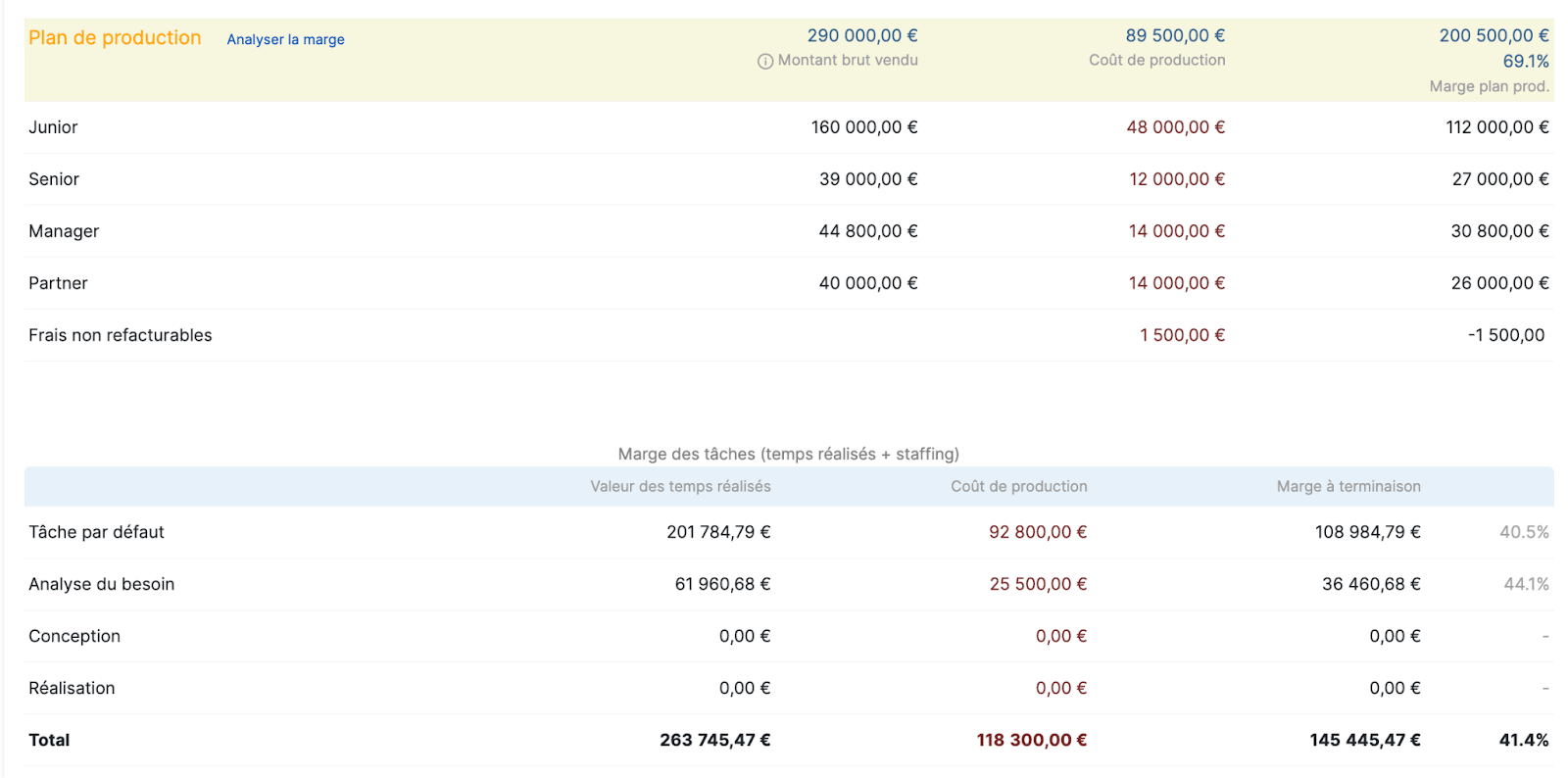
For this, Stafiz offers, for example, a production plan.
It aims to visualize the expected margin by profile or by phase.
Thus, it offers a precise vision by taking into account all costs (purchases, subcontracting costs, human resources costs depending on seniority, etc.)
Step 5: Select the most suitable profiles
The selection of profiles is essential in a project.
In fact, it has a major influence on resource allocation, budget and schedule.
A flawed selection can lead to lost productivity and unforeseen costs.
Finding the balance between availability, appetite and budget
Thus, selecting profiles for a project involves finding the right balance between skills, availability, appetites and costs.
Be careful, don't neglect appetites: a demotivated or passive employee could slow down the project or damage your reputation.
In addition, be vigilant about the availability of the resources selected on the project to prevent profiles from cannibalizing each other.
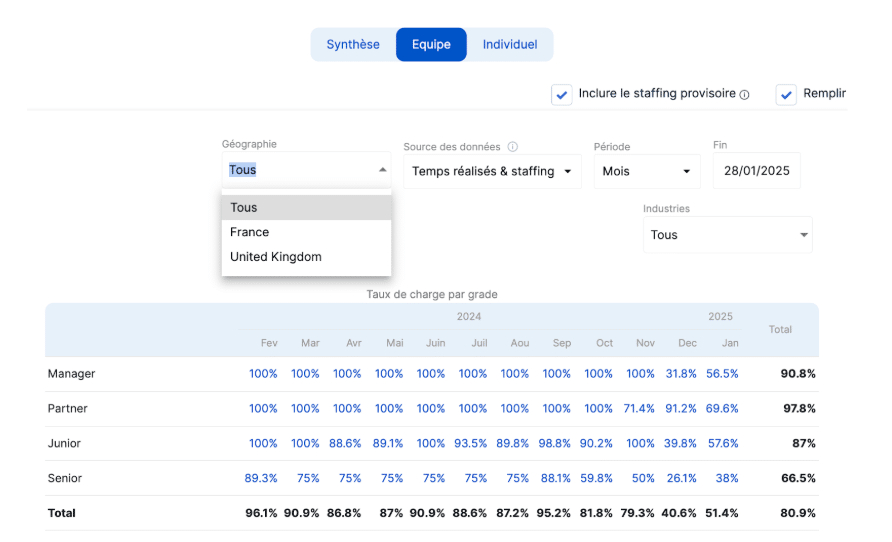
Use tools: matching engine and scenario builder
To select profiles strategically, cross-reference the data available.
Stafiz offers two features that are ideal for selecting profiles: the matching engine and the scenario builder.
Stafiz's Smart Matching highlights project/profile compatibilities by taking into account availability, skills and motivation.
In addition, it can be particularly useful for IT Services because it helps to identify potential profiles for a management company according to defined criteria.
Identified profiles can then be contacted directly in order to anticipate positioning.
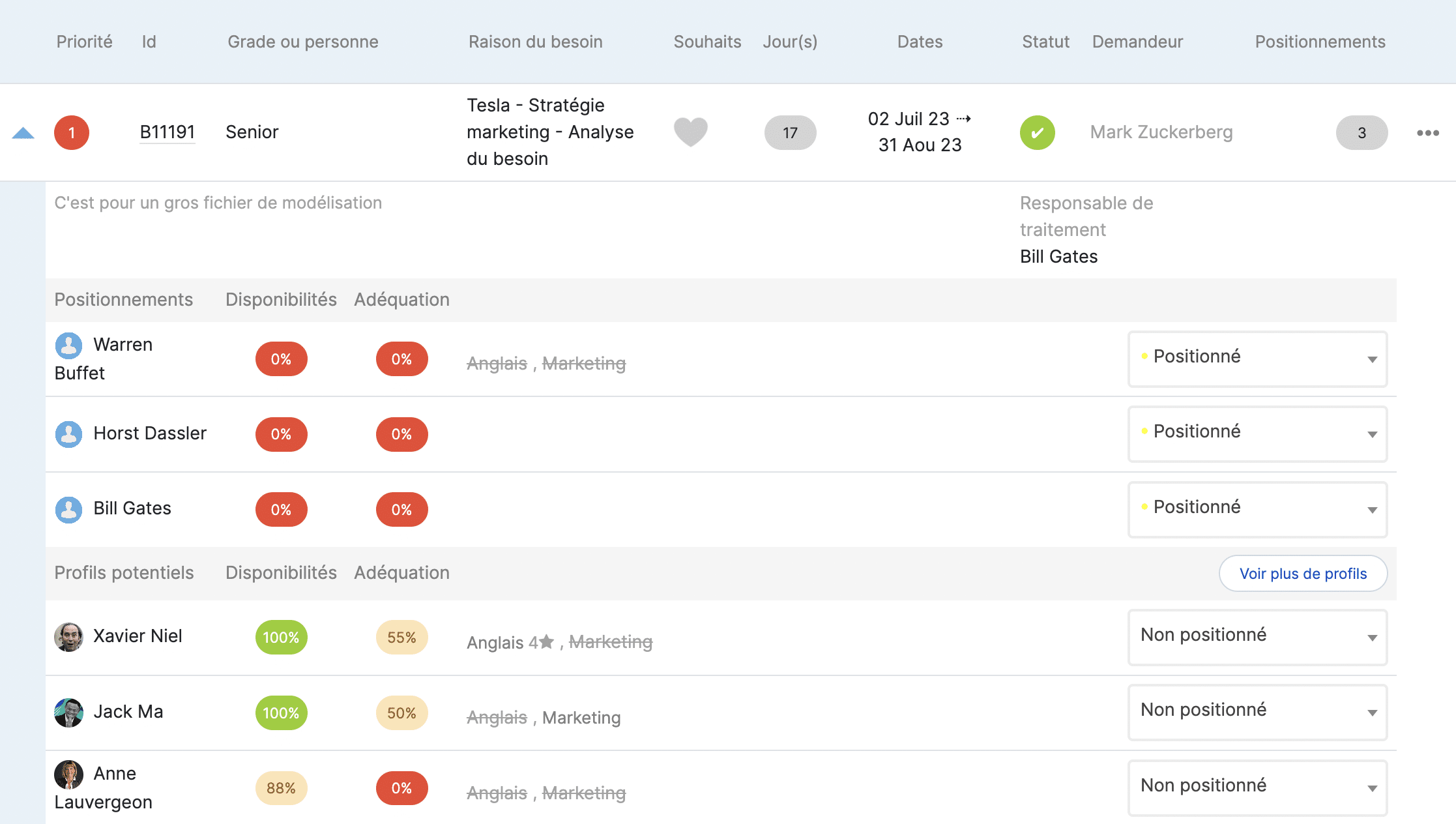
In addition, the resource planning grid allows you to see which profiles are best suited to your upcoming projects.
This feature helps to arbitrate to strategically place each profile.
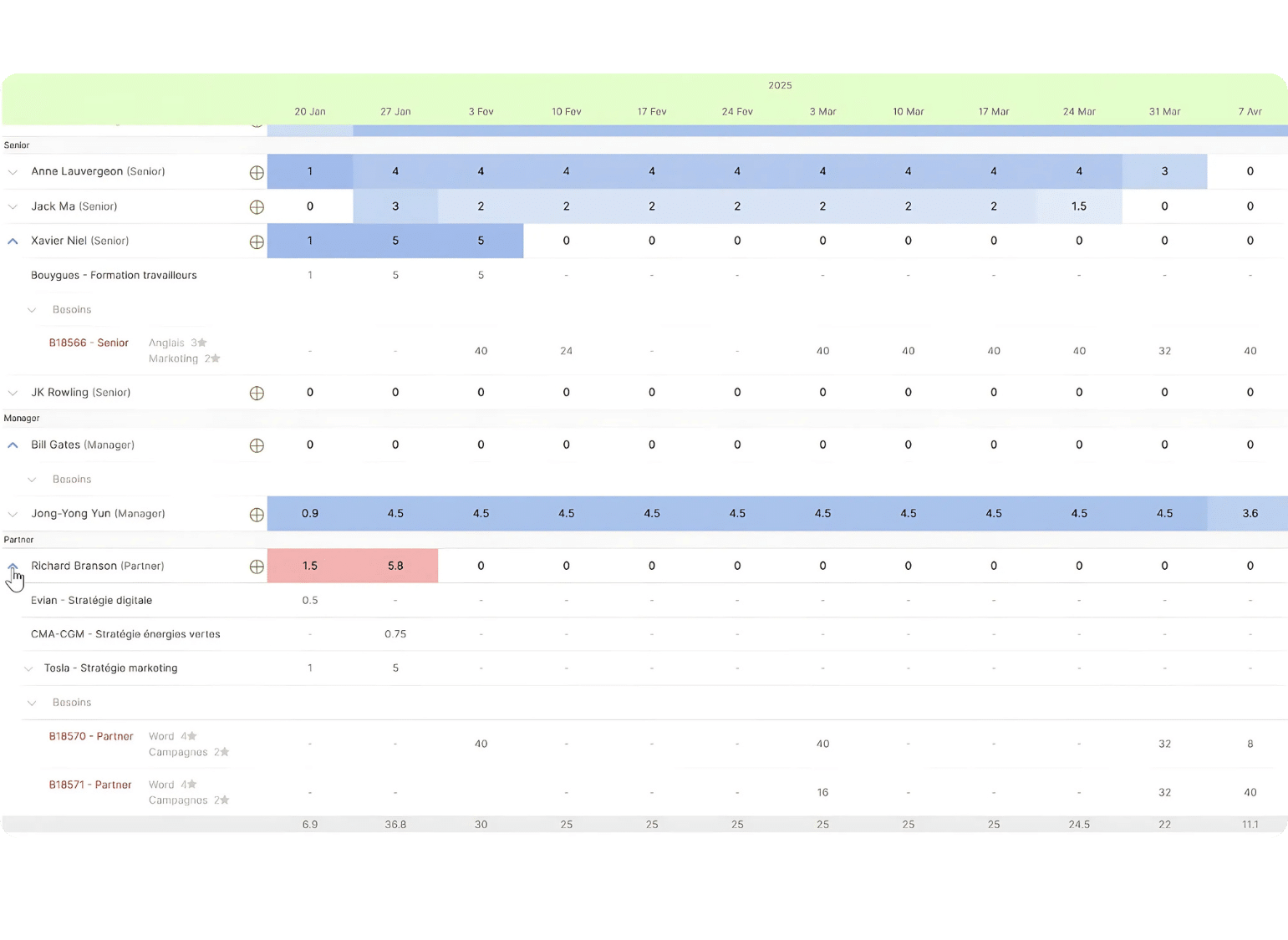
A powerful search engine
You can also search for a profile to position on an assignment by typing keywords for skills, role, experience, or any other data that seems relevant to you.
The other profile selection tool, the scenario builder allows you to optimize your investments.
You can choose the most suitable profiles according to their relevance, expected margins or occupation rates in order to maximize profitability.
Optimize sales performance
This type of feature optimizes sales performance in three areas.
- The overall profitability, as employee workloads are optimized.
- Commercial performance and customer satisfaction because projects are well executed, thanks to adapted profiles.
- Employee commitment and retention because aspirations are taken into account.
Step 6: Define resource allocation
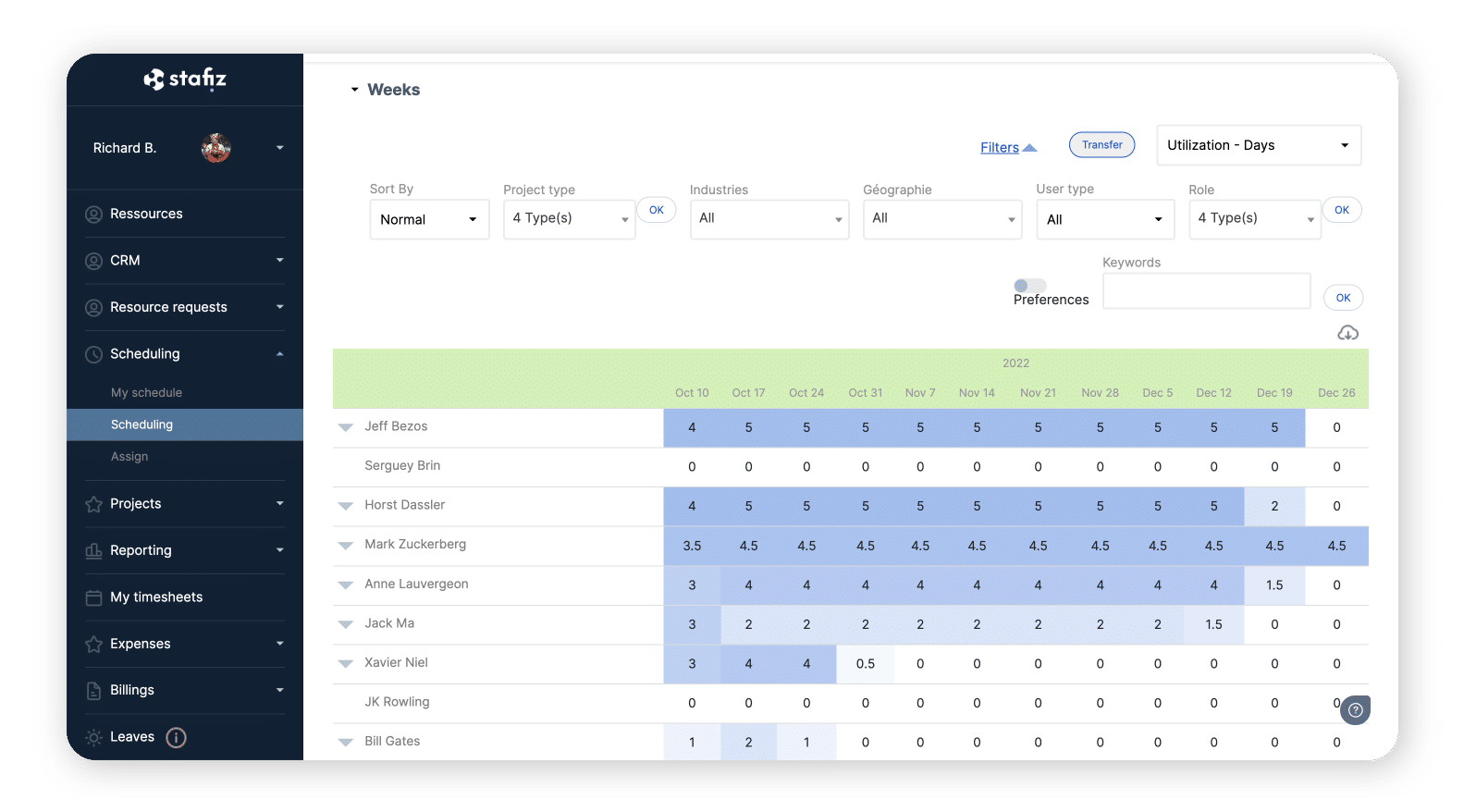
Getting a realistic view of capabilities
To allocate resources strategically and thus enable the project planning clear, reliable data is essential.
Thus, having a real-time view of capabilities facilitates decision-making.
One feature of Stafiz is to propose a pre-resource planning to facilitate deliberations.
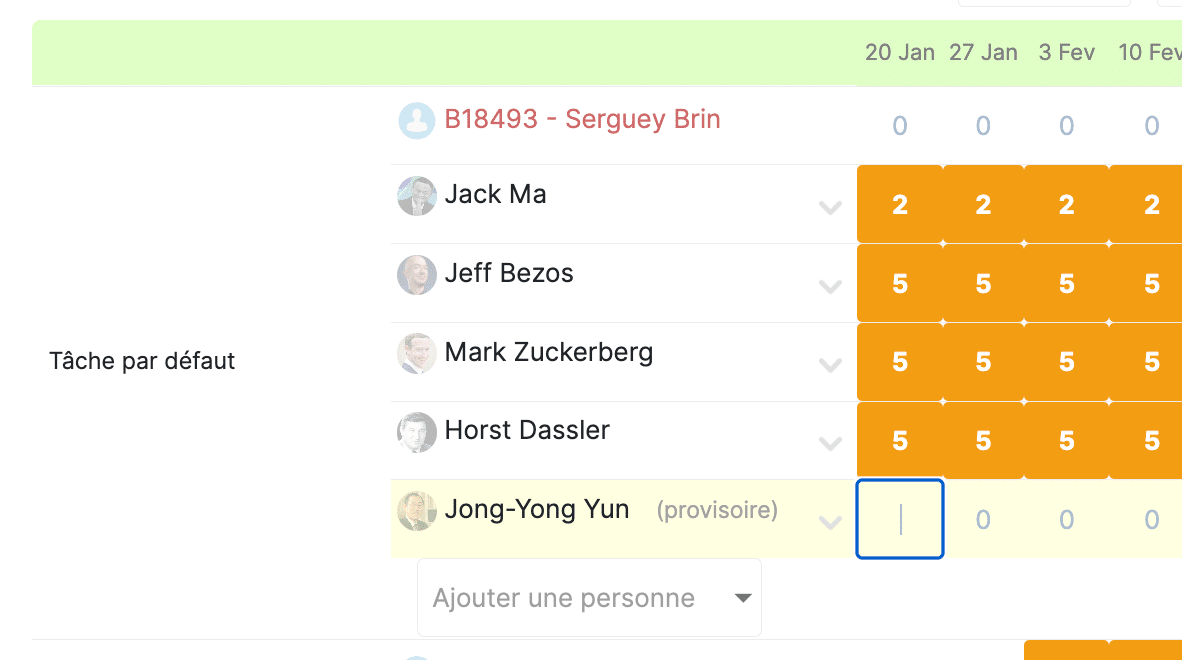
This then takes into account criteria such as leave, training or part-time work.
Define roles and responsibilities
The next step is to determine everyone's roles and responsibilities in order to avoid misunderstandings or conflict.
Indeed, each employee must know at what stage he or she is involved and what is expected of him or her. Failure to do so could jeopardize the project schedule, and therefore the success of the project as a whole.
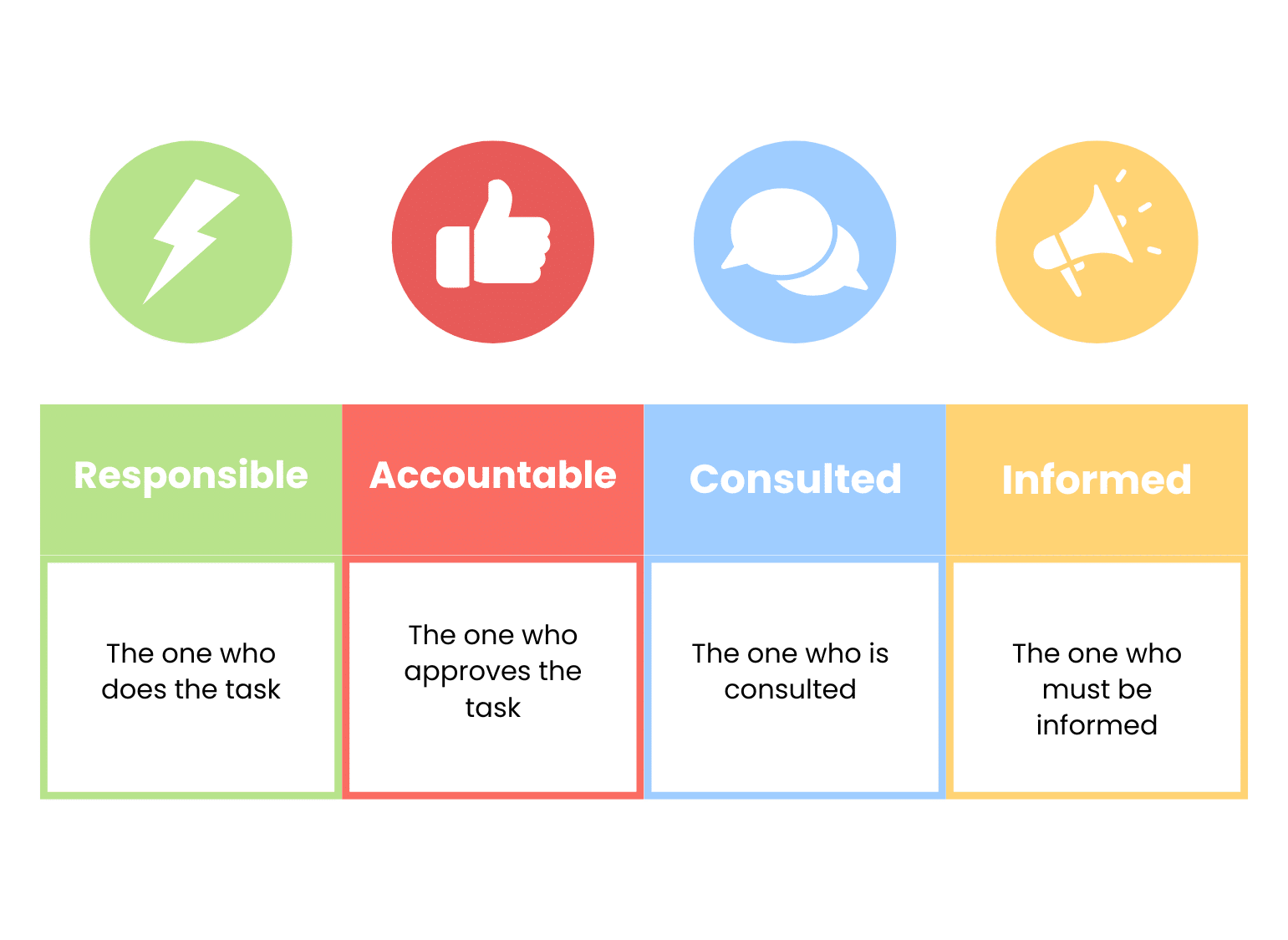
Tools facilitate this step, such as the RACI matrix. This makes it possible to clarify who does what, when, and what is expected of him.
Step 7: Link planning, human resources and budget
Several steps are interdependent and must be carried out in parallel.
This makes it impossible to draw up a budget without knowing the tool to be used, the number of collaborators, or the scope of the tasks required to complete the project.
In the same way, it is difficult to decide on the size of the team without having an idea of the budget.
So, you can start by estimating the number of hours and collaborators needed for each task.
Then, consolidate the whole thing to establish a schedule.
The Gantt schedule is still a credible option, but a comprehensive project management tool will be easier to update.
However, planning is not a tool frozen in time: it is flexible because it will evolve with the reality of the projects.
Step 8: Evolve the project schedule
Indeed, the schedule evolves as the project progresses, hence the importance of rigorous project monitoring.
Stay Flexible
The project schedule must be adapted to the constraints of the project.
Thus, it is not uncommon to observe unforeseen events in consulting or IT.
In addition, external events may require adjustments (restructuring, legal developments, wars, etc.).
This is why it is essential to implement effective risk management before any project starts.
This need for flexibility implies the need for reliable, centralized information. This guarantees a consistent level of information which facilitates reactivity in the event of discrepancies.
Set up checkpoints
Project monitoring involves checking three essential points:
- costs,
- resource allocation,
- the deadlines.
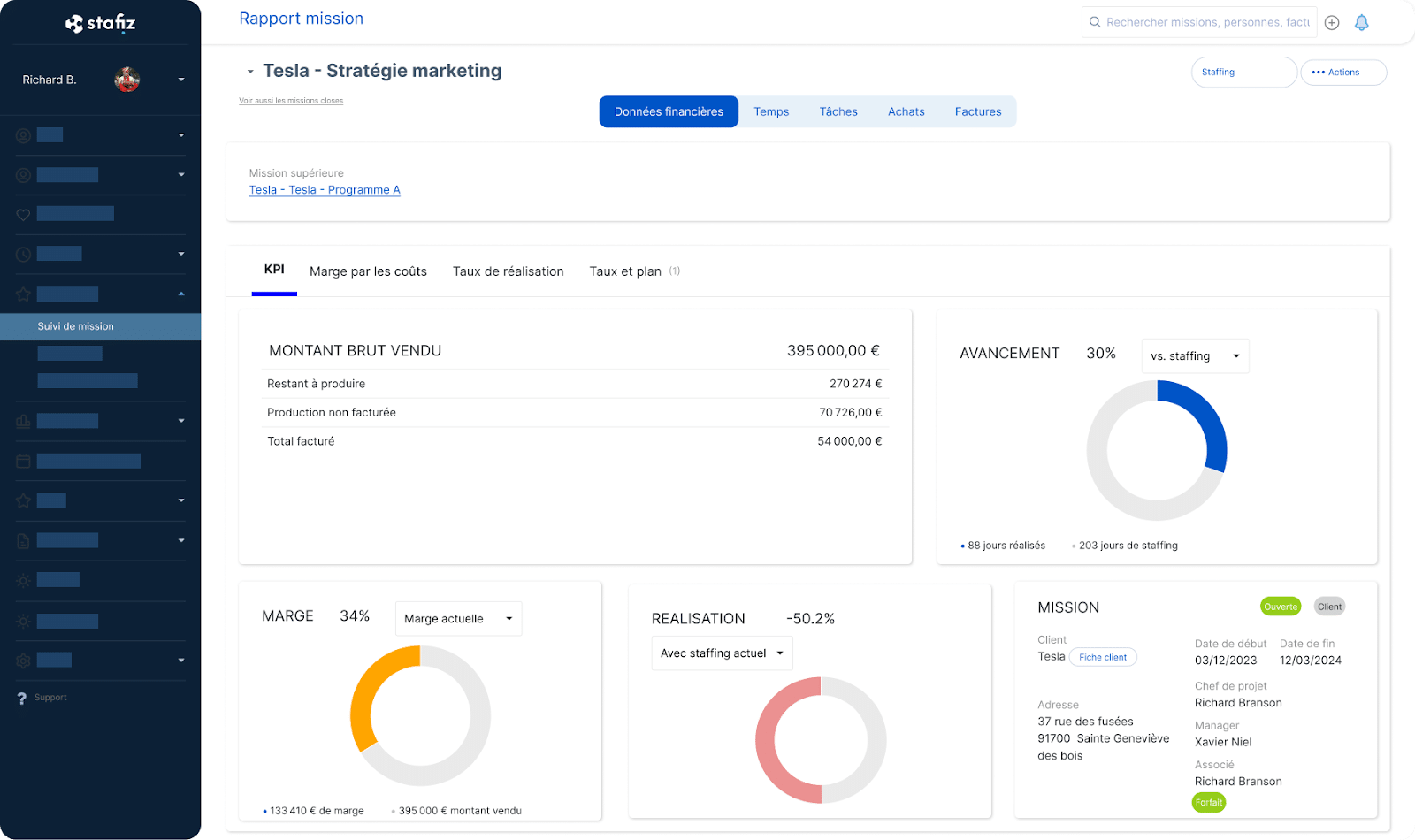
Stafiz offers functions for track costs such as :
- a forward-looking vision;
- the expected financial landing in the event of a change in resource planning, tasks, or budget;
- Consolidated data for all teams, with dedicated views by department (e.g. specific views for finance)
In addition, other features are also used to control the distribution of resources.
- Re-scheduling resources (in case of underload or overload) and identification of availability.
- Visualization of the resource planning on non-billable projects to reassign profiles.
- Optimization of reassigned assignments : possibility of modifying schedules in a few clicks (example: postponement of invoicing deadlines).
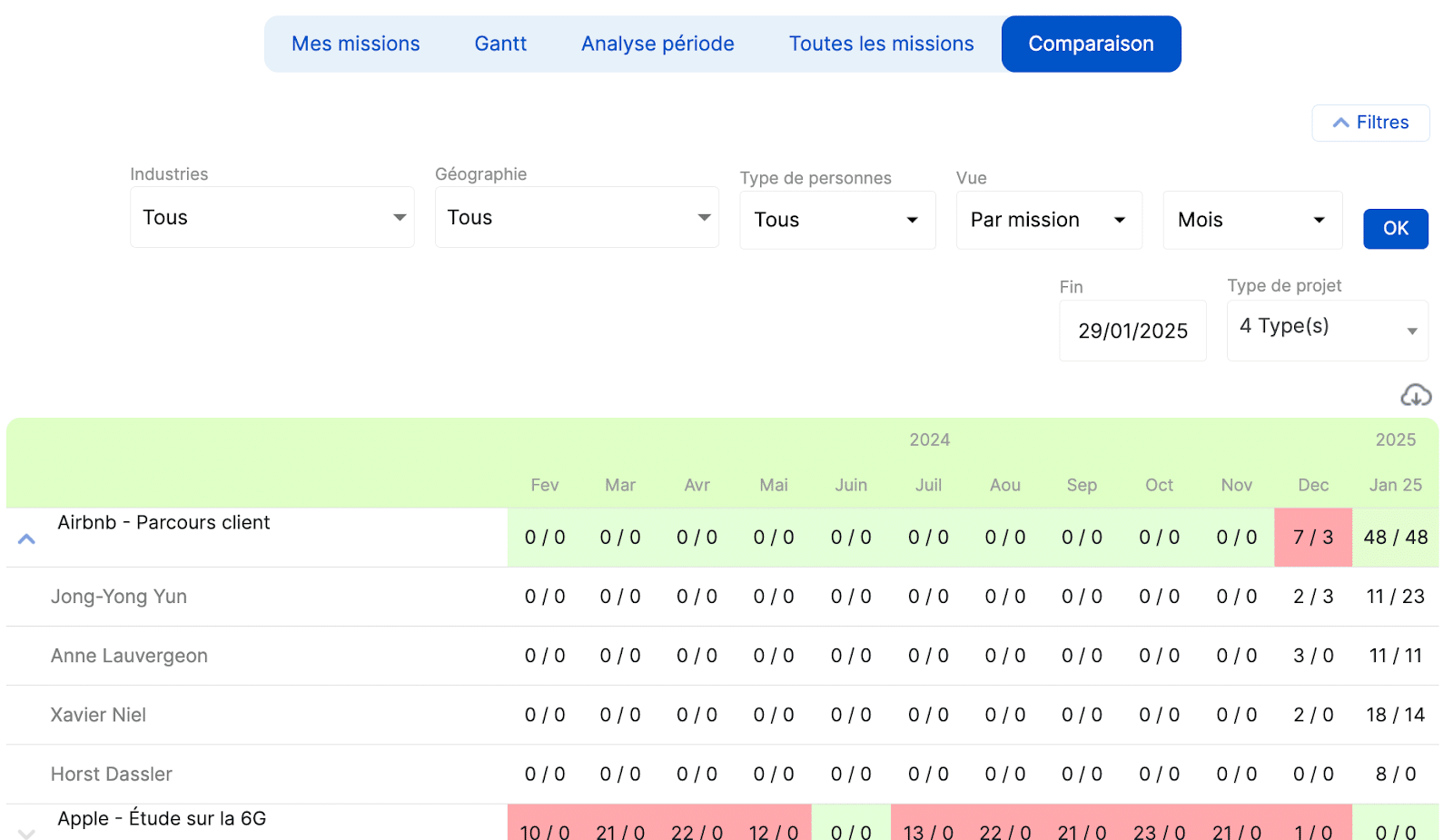
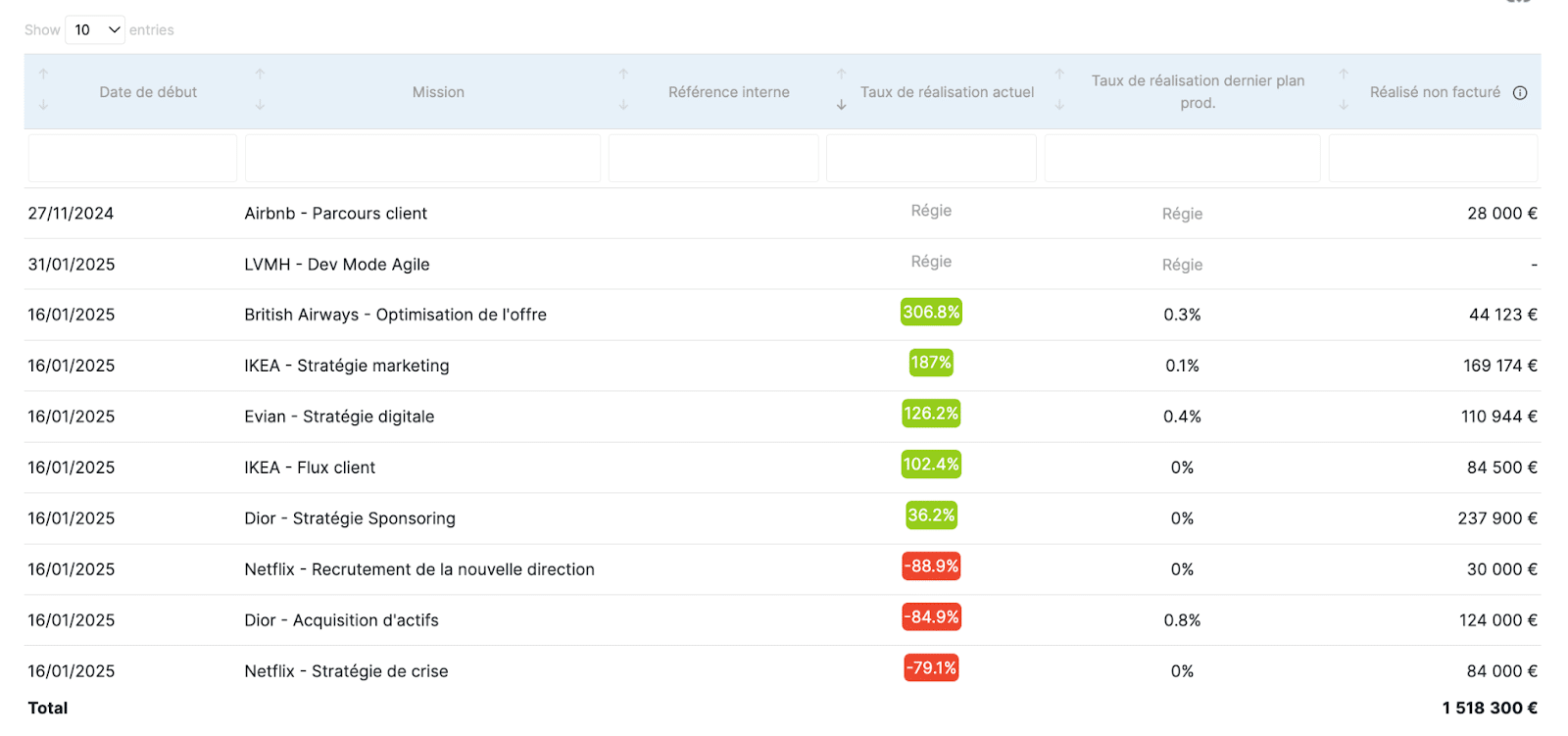
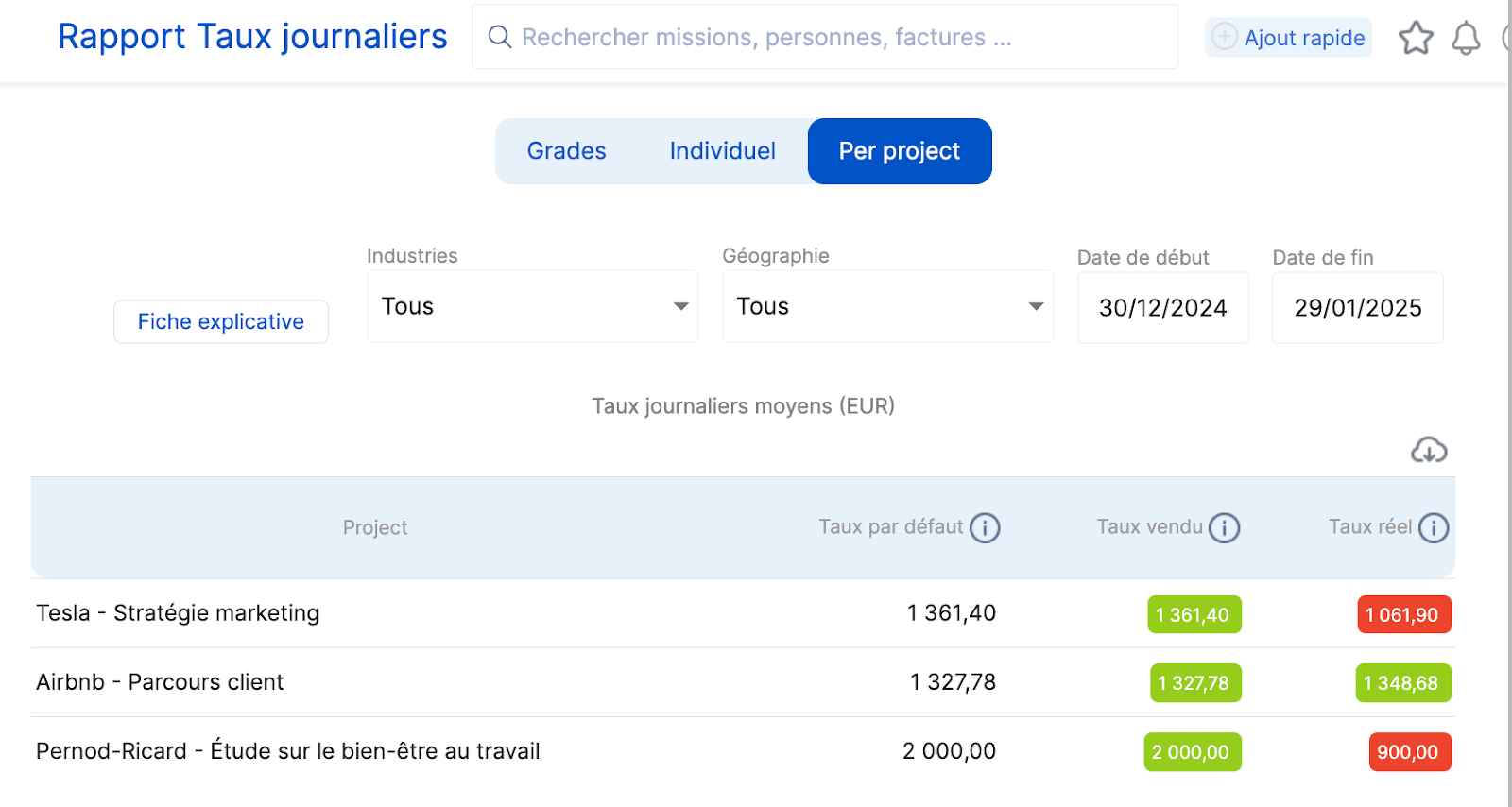
Align teams
The implementation of a project schedule also serves to align the teams, post-project.
Indeed, the centralization of data makes it possible to align the project, finance and HR teams, who have a clear visibility on the objectives achieved.
Thus, each department can have the details of each profile per project .
Project planning is one of the pillars of project management. Indeed, it impacts all aspects of the project: financial, time, resources.
However, setting up an effective project schedule cannot be improvised. This document must be prepared rigorously, but it is a living document, varying over the course of the project.
Our final advice: use existing templates, tools and methods to save time, and involve the teams! This will boost their involvement and help you build a realistic and relevant project schedule .
Questions:
Adapting a project schedule in the event of unforeseen events is based on three key pillars: anticipation, flexibility and communication.
- Set up real-time monitoring: use project management tools (ERP, Gantt, Kanban, etc.) to quickly identify discrepancies and adjust tasks accordingly.
- Prioritize and replan: Assess the impact of changes on time, resources, and budget. Adjust the schedule according to the priority objectives and available constraints.
- Review resource allocation : If an unforeseen event impacts the workload, reallocate resources based on availability and required skills.
- Maintain smooth communication: Quickly inform stakeholders and involve them in decision-making to ensure optimal responsiveness.
- Allow for flexibility: Integrate time and budget buffers from the outset to absorb unforeseen events without compromising the project.