DOSSIER - EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INVOICING FOR SERVICE COMPANIES
1. How do I estimate the costs, prices, and billing type for a billable project?

In this article of our invoicing file for service companies, we start at the beginning of the invoicing process: the costing of your projects. Discover the links to all the articles in the dossier below:
1. How do you estimate costs, prices, and billing type for a billable project?
2. How to manage the risks of project overruns?
3. How can I get paid faster by customers?
4. How to manage complex billing arrangements
5. How do I take into account the invoicing of taxes? What about multi-currency billing?
6. How to manage invoicing between different entities of the same company (intercompany flows)
7. How can we simplify communication with customers?
8. How can I modify certain parameters that will impact invoicing during projects?
9. How to set up a project quoting and invoicing tool?
Before even invoicing, the project must be costed with the greatest precision and the margin must be estimated in order to determine the right price level. The first step is to list all the resources needed to carry out the project and the workload to deliver it.
Define all the necessary resources
i. Employees and associated time
You have to start by listing the profiles that will be necessary to carry out the project. For each profile, it is necessary to estimate the time required to carry out the project as defined to date. This estimate must be as realistic as possible, even conservative, to avoid unpleasant surprises.
ii. Outsourcing
Many projects require the use of subcontractors. Regardless of their contribution, it is necessary to plan for subcontracting purchases and define the re-invoicing approach. Subcontracting may be invisible to the customer, or it may be invoiced clearly, with the possibility of making a margin on this subcontracting.
iii. Other purchases
You have to think about all the other purchases. Some projects require buying and reselling products (e.g., computer licenses) or hardware. To properly anticipate the invoicing of the project, these elements must also be taken into account when thinking about the invoicing approach.
iv. Fees
When travel is required to carry out the project, the associated costs must be estimated. Actual rebillable costs do not impact the margin, but must appear in the invoices. Non-rebillable fees have a direct impact on the margin.
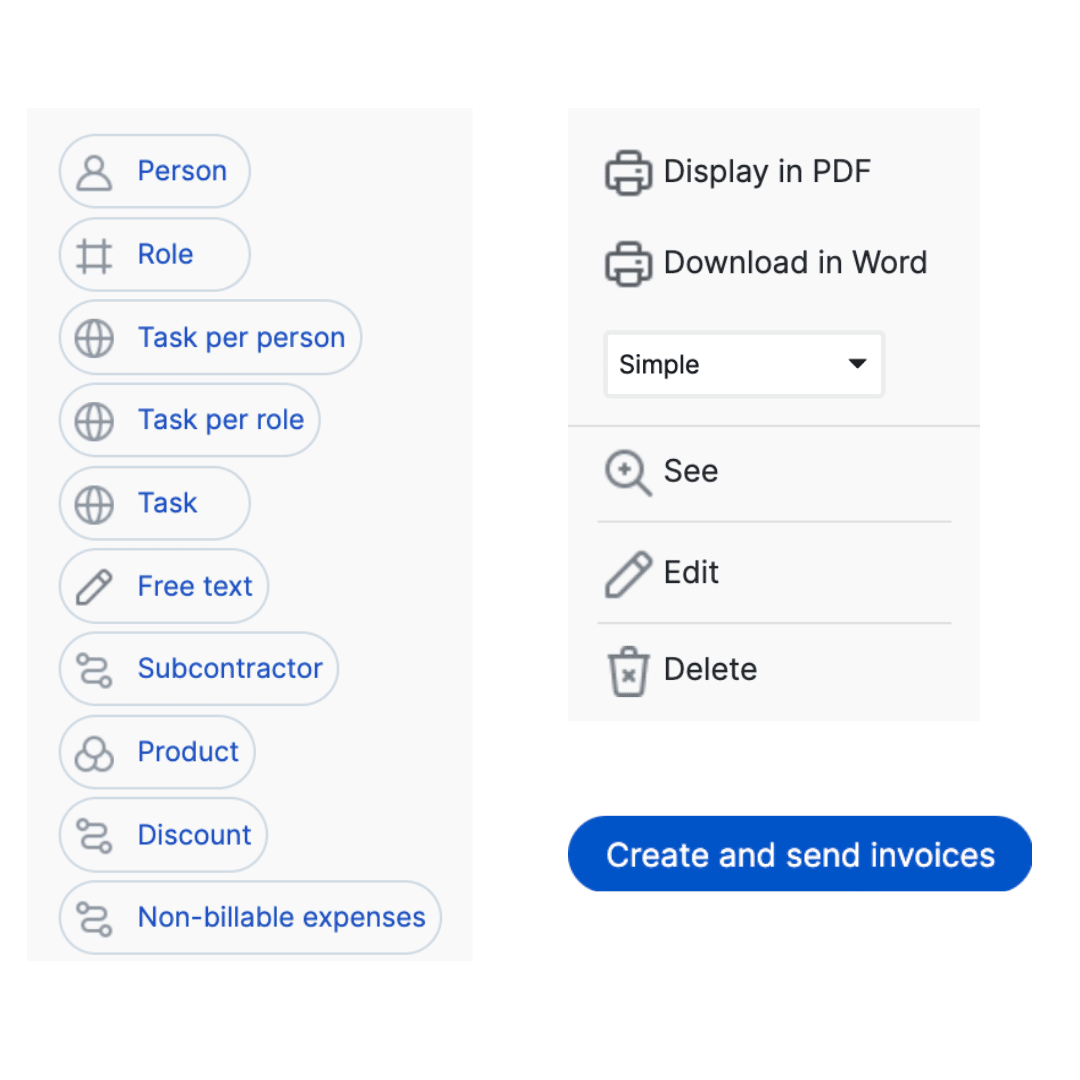
To facilitate project invoicing, Stafiz offers agility to define all types of elements to be integrated into an invoice.
Stafiz's invoicing can simply include man-hours/days, quantities, subcontracting or costs.
The agility of the invoicing module makes it possible to set up the details for each project.
Setting an adequate selling price
To invoice a project, the client must first have accepted your offer. The pricing to be invoiced for a project is strategic, but it must reflect clear standards. Without a standard, prices are set in an anarchic manner and may lead to lower profitability.
i. Rely on standard prices
Setting standard prices is a prerequisite for easy project invoicing.
Each contributor profile, each type of subcontractor and product must have standard rates shared with the sales teams. These standard prices must be known to all the teams working on commercial offers, and when they change (annual increase for example), changes must be communicated.
These standard prices are a basis on which sales reps can be assigned a trading window based on activity and time period.
ii. Calculate the projected margin
Standard prices are used to calculate turnover. To calculate the margin, you also need to define the costs of each element.
To simplify margin analysis, it is a good practice to define standard costs, especially for internal profiles. On the other hand, subcontracting costs and fees often depend on each project. It is therefore necessary to calculate them by knowing the details of the project to be carried out.
By deducting the costs necessary to carry out the project from the turnover, the project margin makes it possible to verify that the project is financially viable: that it reaches the expected profitability standards.
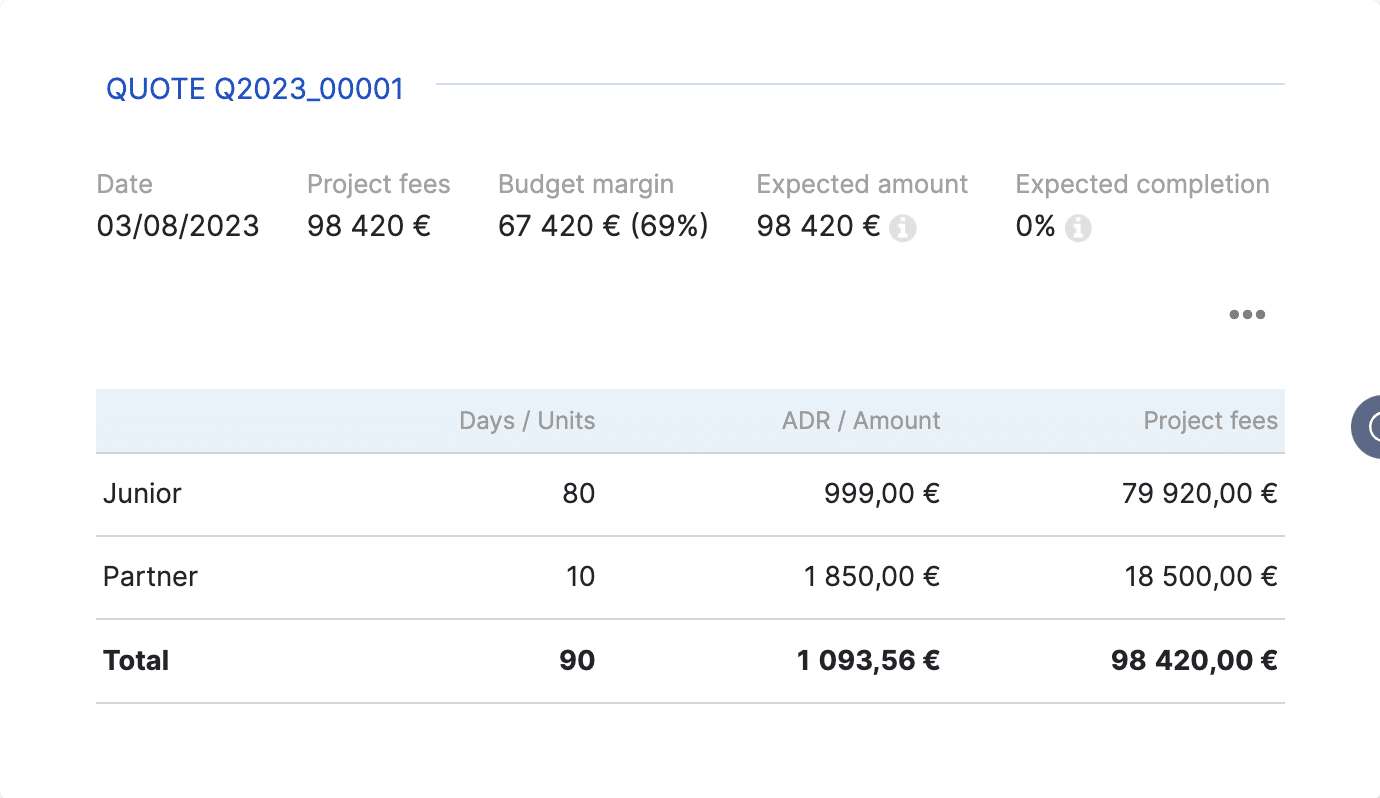
Costing with margin from pre-sales
Stafiz integrates standard prices and costs into its commercial module. Results, you can create the quotes in Stafiz, edit them and send them to your customers. And Stafiz also tells you the margin you make according to each quote. This helps to avoid starting projects that are too risky.
Choose the right billing type
The type of invoicing varies depending on the type of project, and the negotiation with the client. Each type of billing has advantages and disadvantages.
i. Billing by time spent or by direct management
This is the most standard billing in professional services. The service is invoiced on a time-by-time basis, based on an agreement on the price per hour or per day.
This is called the Hourly Rate or Daily Rate.
On the one hand, this type of invoicing simplifies the negotiation with the client and avoids risk-taking by the company selling the project. The rates are transparent, and the project's margin is almost guaranteed.
Nevertheless, billing by time spent prevents the company from outperforming. It is attached to the time spent by employees who have no more than 8 hours of work per day. So it limits the potential. It does not value excellence in execution, automation of tasks and the creation of value for the customer.
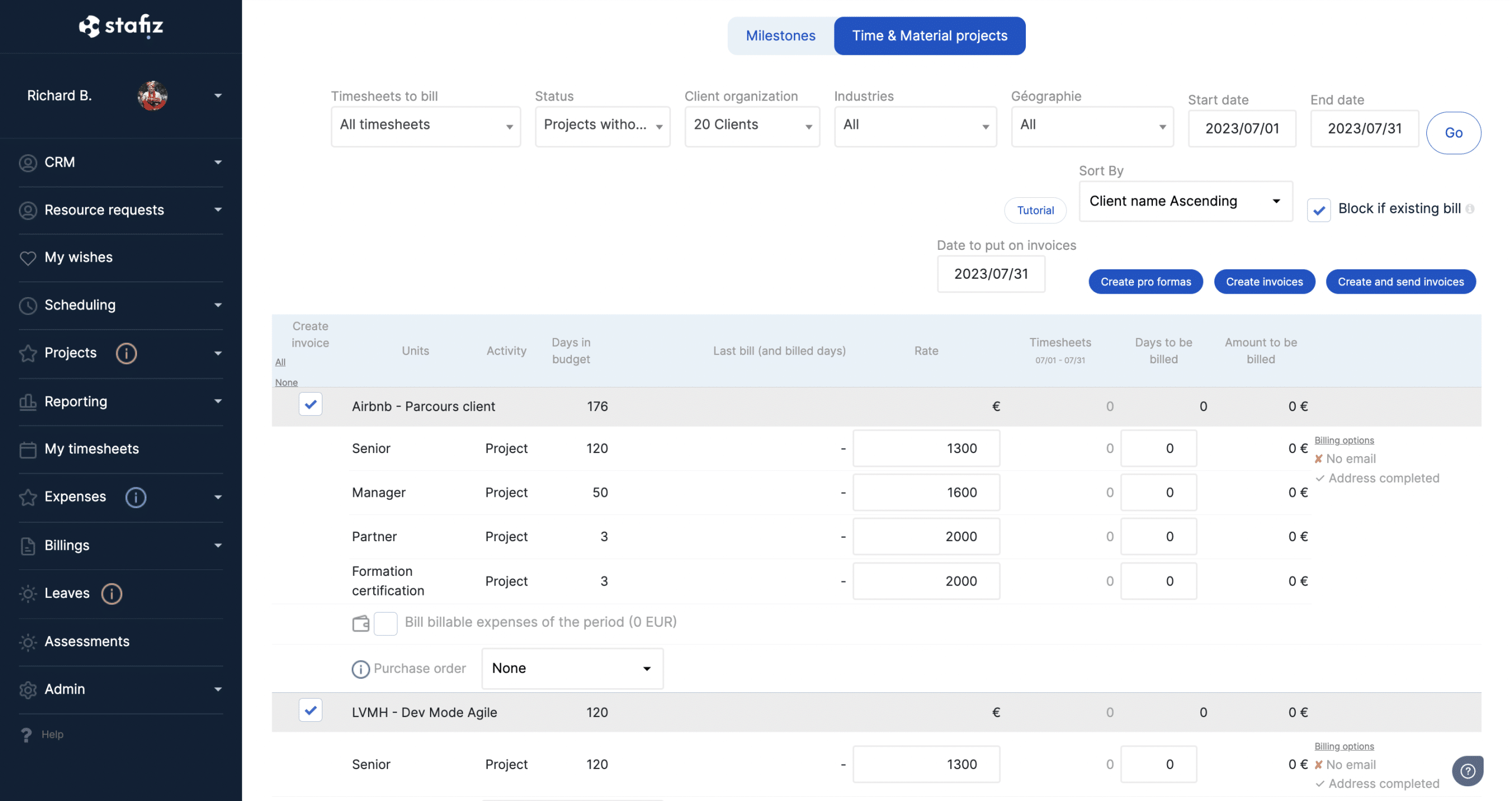
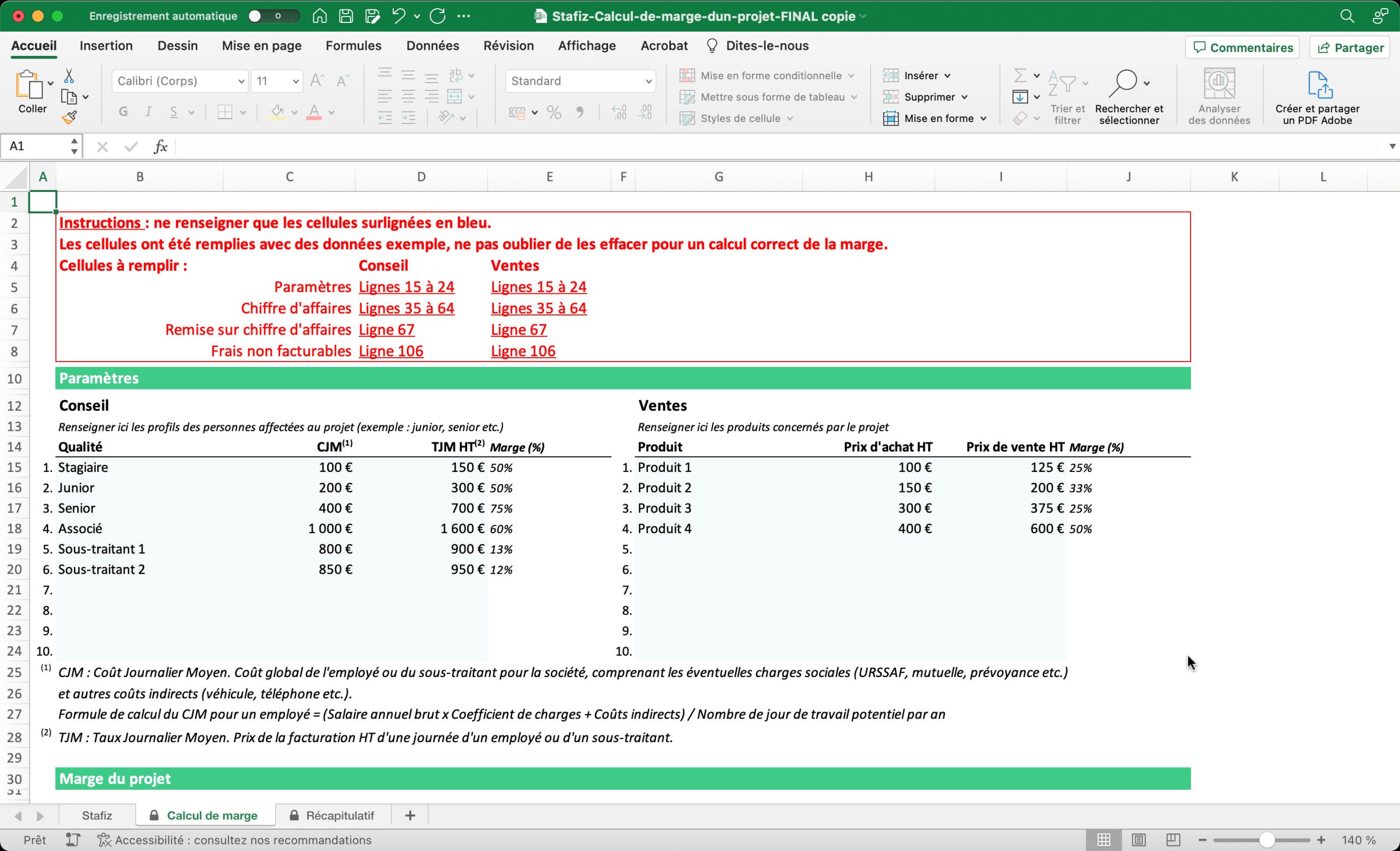
To facilitate your project budgeting, Stafiz provides you with a project budget table template for:
– Have a view of your KPIs
– Check the viability of your projects
– Arbitrate on the allocation of your resources
ii. Flat-rate billing
Flat-rate billing corresponds to invoicing at a fixed amount negotiated with the customer. This amount can be invoiced in several instalments, according to a schedule negotiated between the client and the company selling the project.
It has the advantage of focusing on the value that the project brings, i.e. its return on investment, rather than valuing only the work necessary to obtain it. This specificity allows for more profitable pricing and therefore higher margins.
On the other hand, when invoicing at a fixed rate, it is imperative to accurately monitor the projected margins of the projects. Otherwise, there is a significant risk of regularly deviating from the budget and missing your objectives.
iii. Subscription billing
Subscription billing is a type of billing in which a company offers a service that can be variable based on an amount negotiated with the customer and invoiced periodically.
Subscription billing provides readability and consistency for the customer who is not surprised when they receive the invoices. It is a form of insurance that allows the service provider to optimize its profitability while remaining at the level of service expected by the customer.
But if poorly managed, the subscription bill can quickly present risks for the issuer. If the contract is poorly put together, the costs, which are variable, can put the project at a loss.
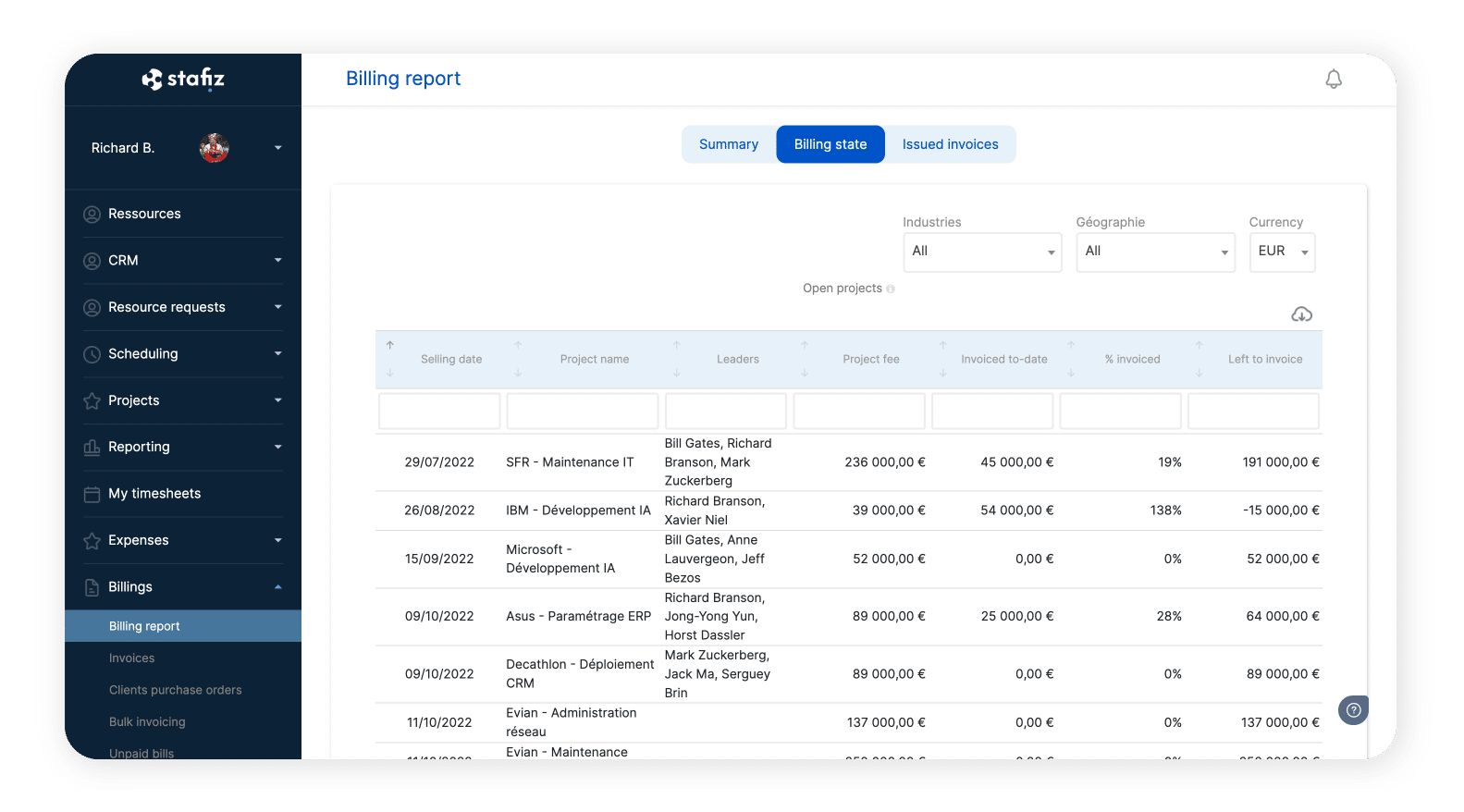
iv. Hybrid Billing
Some projects require a mix of these different approaches. Let's take the example of a software deployment project. It regularly happens that the invoicing of the project is invoiced at a fixed price, with the exception of certain custom developments which are invoiced by time spent. Then once the project is installed, a subscription for monitoring and maintenance can be charged.

Stafiz allows you to manage all invoicing and automate each of them.
Flat-rate billing, time-based billing, subscription or hybrid billing.
Regardless of how the project is invoiced, Stafiz makes it possible to calculate turnover and margins in the right way.
The 9 problems of project invoicing and how does Stafiz help you solve them?
1. How do I estimate the costs, prices, and billing type for a billable project?
2. How to manage the risks of project overruns ?
3. How to get paid faster by customers?
4. How to manage complex billing arrangements
5. How do I account for tax invoicing and multi-currency invoicing?
6. How to manage invoicing between different entities of the same company (intercompany flows)
7. How to simplify communication with customers?
8. How can I modify certain parameters that will impact invoicing during projects?
9. How do I set up a project quoting and invoicing tool?